Why are children in Hong Kong distinctly shorter in height than those in Beijing, China?
Hiroshi Mori*
Professor Emeritus, Senshu University, Tokyo, Japan
Received Date: 15/11/2023; Published Date: 16/04/2024
*Corresponding author: Hiroshi Mori, Professor Emeritus, Senshu University, Tokyo, Japan
Preface
For the past few years, the author has examined the height development of children in Japan in comparison with those in South Korea and China in the North-Eastern part of Asia. Despite a lasting stagnation of the macro-economy in the 1990s and 2000s, Japan was still much greater in respect of per capita GDP than South Korea and China. Children in Japan were overtaken in mean height by 3-4 cm by their peers in South Korea and China in the mid-2000s. With respect to per capita consumption of animal protein, Japan was distinctly greater than South Korea and China then. Have Japanese children depleted their “gene-potential” in height in the 1990s [1]? The author declined to accept this hypothesis [2].
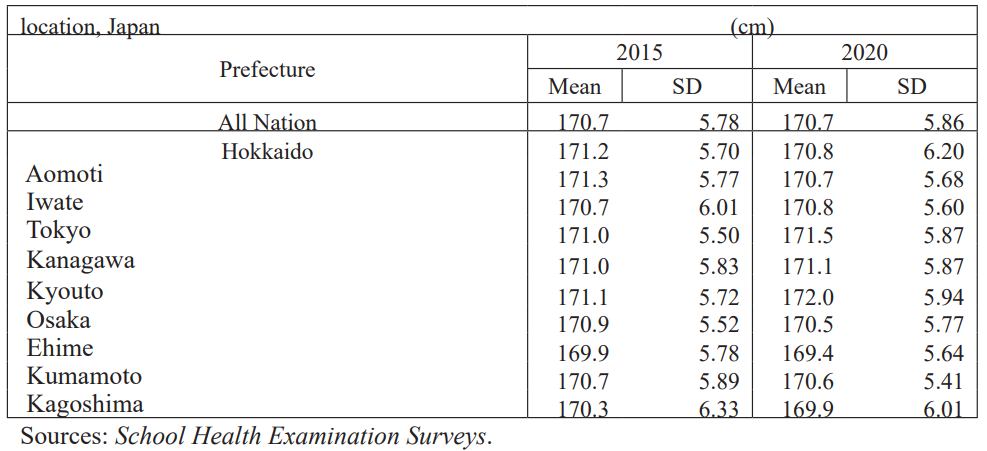
A half century ago, the author was working on the marketing of fruit and vegetables, apples and mandarins, in particular. He would visit the northern prefectures of Japan for apples and southern prefectures for mandarins, and conceived the general picture that people in the North were lighter in complexion and taller in height than those in the South. However, when referring to School Health Examination Surveys, conducted by Ministry of Education in all prefectures every year [3], no differences in mean height of school children by grades are observed by latitude in recent periods in Japan (Table 1).
Table 1: Average height of high school senior boys.
Questions
We would often hear that people are diverse in China: northerners are taller than southerners and urban residents are taller than rural people. It was only a few months ago that the author came across the statistics that there do exist huge disparities in average height between provinces in recent years [4]. In respect of mean height of male youth, Beijing is 175.3 cm and Guangdong in southern China was 169.8 cm, respectively in 2015. In the case of female youth, Beijing was 167.3 cm and Guangdong was 159.8 cm, respectively. Regarding ethnic compositions, both Beijing and Guangdong are predominantly Han areas: Han occupies 97% and 99% of the two districts (Table 2).
China suffered from the Great Famine in the end of the 1950s caused by the Great Leap Forward [5]. China’s per capita food supply was meager at 1,500 kcal/day in the beginning of the 1960s and slightly close to 2,000 kcal in the beginning of the 1970s, substantially less than Japan and South Korea, 2,700 and 2,800 kcal, respectively [6]. R.H. Steckel stated in Jr. Econ. Literature, 1995 that stature is a net measure that captures the supply of inputs to health [7]. In regard to caloric intake, it is unlikely that people in the entire country of China could have been taller in mean height than either Japanese or South Korean peers in these years. Yet that is what the available data show (refer to Tables 3 and 4).
The Ministry of Education, the Government of China initiated nationwide surveys of school children’s stature by age in 1985 and has conducted the surveys every 5 years (Chinese National Survey of Students’ Constitution and Health: CNSSCH) [8]. In view of the fact that the mean height of children should vary by locality as observed above (Table 2), the author is somewhat suspicious about the validity of the national average statistics (China is as large as Europe from north to south and west to east).
Looking for secular changes in mean height by specified localities, the author came across the data for Hong Kong, which looked plausible [9]. Hong Kong, predominantly Chinese in population, was returned to China from Great Britain in 1997. In respect of per capita GDP, HK was nearly 10 times as big as mainland China, as a whole in 2000 and even in the mid-2010s HK was more than 5 times as big as mainland (Table 3). As of 2015, HK was not among the China’s tallest provinces in respect of mean height of residents, either male or female. In terms of average height of residents (youth), male and female, Hong Kong, were 170.9 and 160.9 cm, respectively, substantially shorter than Beijing (175.2 and 167.3 cm) and Shanghai (173.8 and 163.8 cm), for example (refer to Table 2 for greater details).
Table 2: Mean Height of Youths by Provinces, China, 2015, upload. Wikimedia.org

Table 3: Changes in per capita GDP, HK, CN, Japan.
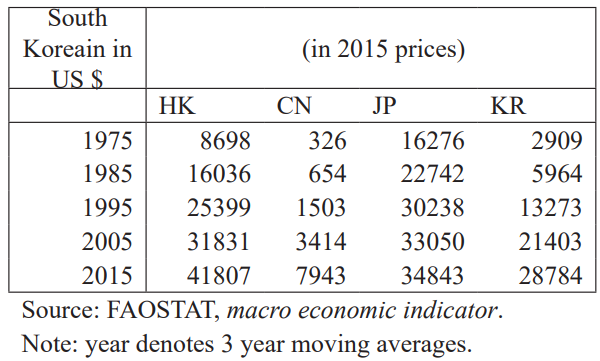
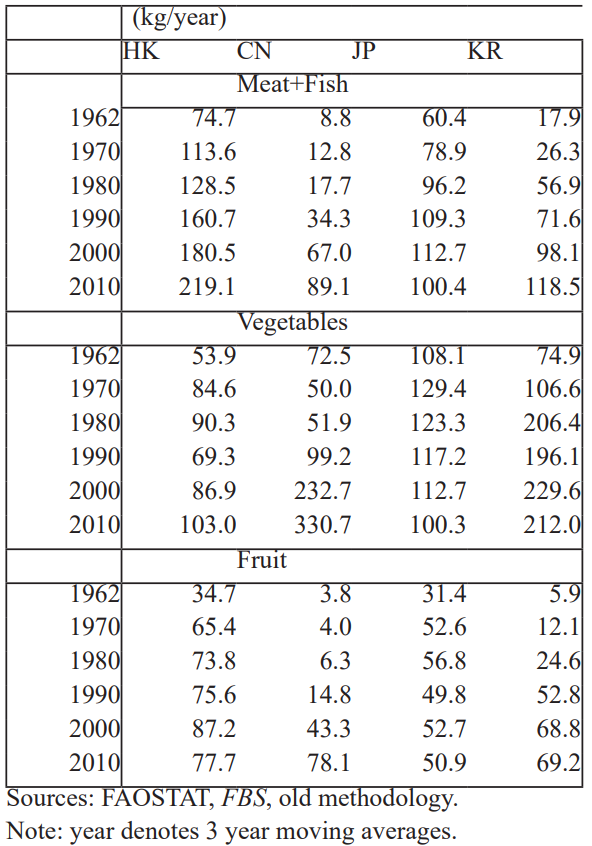
Table 4: Changes in per capita supply of meat+fish, vegeta- bles and fruit, HK, CN, JP and KR, 1962 to 2010.
Proposing Hypotheses
Table 4 depicts structural changes in food consumption over the past half century, in Hong Kong, Mainland China, Japan and South Korea. HK has been the greatest in respect of per capita intakes of (meat+fish), nearly twice as big as Mainland China, Japan and South Korea in the 2000s. What struck the author the most, HK has been very low in respect of per capita consumption of vegetables. Mainland China increased per capita consumption of vegetables from 50 kg in the 1970-80s to 330.7 kg in 2010, whereas HK increased very slowly from 85 kg to 100 kg over the same period. Hong Kong was as low as Japan in respect to per capita consumption of vegetables in the 2000s, one half the level of South Korea and one third that of the mainland China. A high animal protein does not result in increasing body height, if consumption of essential nutrients: vegetables and fruit is insufficient, as stated by Mathias Blum, 2013 [10]; Mori [11,12]. In addition, high levels of GDP per person may not correlate well with body hight.
Acknowledgement: Sincere thanks go to John Dyck, formerly senior economist at ERS/USDA, for his comments and thorough editing.
References
- Kopczynski, Michal. Body height as a measure of standard of living: Europe, America and Asia, Roczniki Dziiejow Spolecznychi I Gospodarczych Tom, 2016; LXXVI-39-60.
- Mori Hiroshi. Have Japanese and South Korean depleted the reserve of gene potentials for body height? J Japanese Medical Research, 2023; 1: 1-5.
- Ministry of Education and Sciences, Government of Japan. School Health Examination Surveys, various issues.
- Height in China, by Provinces, Upload, Wikimedia. Org, on the internet, 2015.
- Ruoran Lu, Xiaopeng Zeng, Jiali Duan, Ting Gao, Da Huo, Tao Zhou, et al. Secular growth trends among children in Beijing (1955-2010), Economics and Human Biology, 2016; 21: 210-220.
- United Nations, FAOSTAT, Food Balance Sheets, 1961~2013, old methodology. ――, FAOSTAT, Macroeconomic Indicators, 2023.
- Steckel Richard H. Stature and the standard of living, J Economic Literature, 1995; XXXIII: 1903-1940.
- Chinese government, Ministry of Education, Chinese National Survey of Students’ Constitution and Health, CNSSCH, 1985, 1995, ---, 2014, 2019.
- Hung-Kwan So, Edmund AS Nelson, et al. Secular changes in height, weight and body mass index in Hong Kong children, BMC Public Health, 2008; 1-10.
- Blum Matthias. Cultural and genetic influences on the ‘biological standard of living’, Historical Method, Jan-Mar, 2013; 46(19): 19-30.
- Mori Hiroshi. Secular changes in child height in Japan and South Korea: Consumption of animal proteins and ‘essential nutrients’, Food and Nutrition Sciences, 2018; 9: 1458-1471.
- Height is a measure of consumption that incorporates nutritional needs: when and what? Clin Med Case Rep, 2022; V9(14): 1-8.

