Relaxing Effect of Mozart's Classical Music on the Autonomic Nervous System and Stress Index in an Elderly Man
Ivan Domuschiev*
Department of Internal Diseases, Multiprofile Transport Hospital, Bulgaria
Received Date: 10/03/2023; Published Date: 14/06/2023
*Corresponding author: Dr. Ivan Domuschiev, Ph.D., Endocrinologist, Multiprofile Transport Hospital, Department of Internal Diseases, Plovdiv City, Bulgaria
Introduction
A person's longevity depends to a large extent on life stressors.
That is why ensuring a peaceful life is one of the decisive circumstances for achieving vital longevity.
It has long been known that good music has a beneficial effect on a person's nervous system and psyche.
Measuring Heart Rate Variability (HRV) is the only accurate quantitative method for studying the autonomic nervous system and determining the human body's response to stress.
Material
The subject of our study is a 61-year-old man, 178 cm tall and weighing 75 kg (BMI =24).
Method
The gold standard for measuring of the heart rate variability (HRV) is the morning measurement immediately after waking up from a night's sleep.
For heart rate recording, we used the "Polar H10" Chest Strap (with Bluetooth BLE signal transmission). The analysis of the results obtained from the heart rate variability (HRV) measurement was carried out with the "Kubios HRV" software.
We took the first (basal) HRV measurement in the morning at 7:30 a.m. immediately after waking up. The examination was performed at complete rest (in a supine position, complete silence and comfortable room temperature). We performed a short term (3 min.) measurement of HRV parameters.
The subject then listens in a supine position for 30 minutes to relaxing classical music by Mozart (Figure 1,2,3).
The second measurement of HRV parameters was made after 30 minutes of listening to this music (Figure. 1A, 2A, 3A).
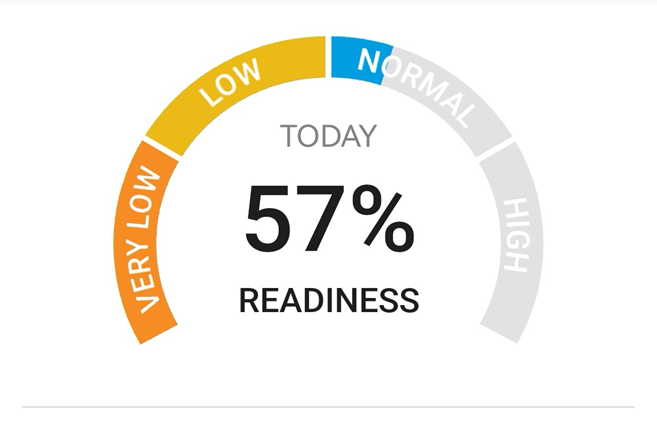
Figure 1: Basal HRV-measurement.

Figure 2: Basal HRV-measurement.
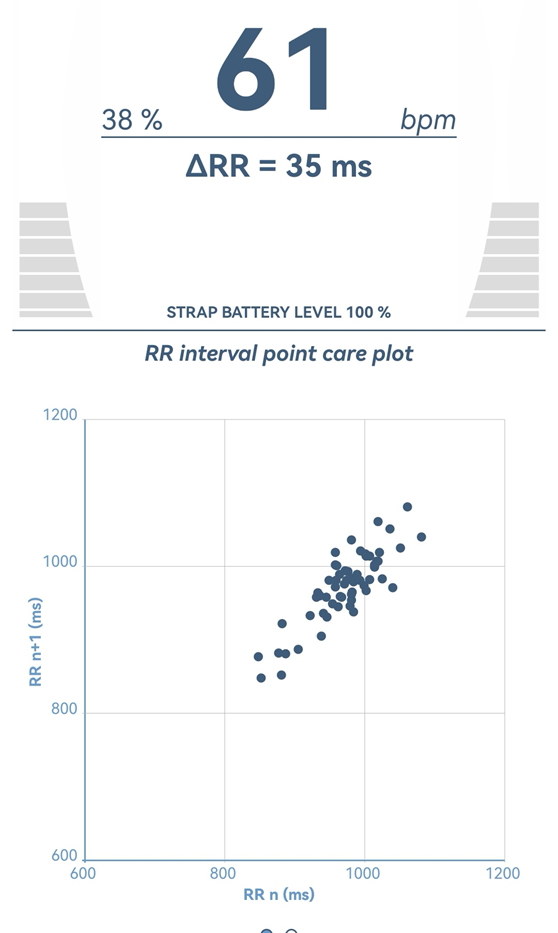
Figure 3: Basal HRV-measurement.

Figure 1A: After Mozart‘s music.
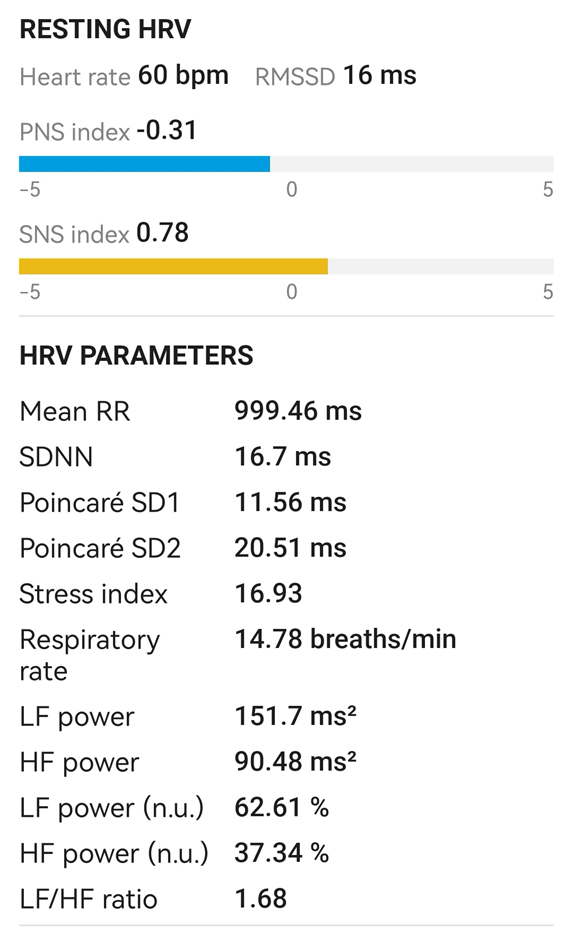
Figure 2A: After Mozart‘s music.
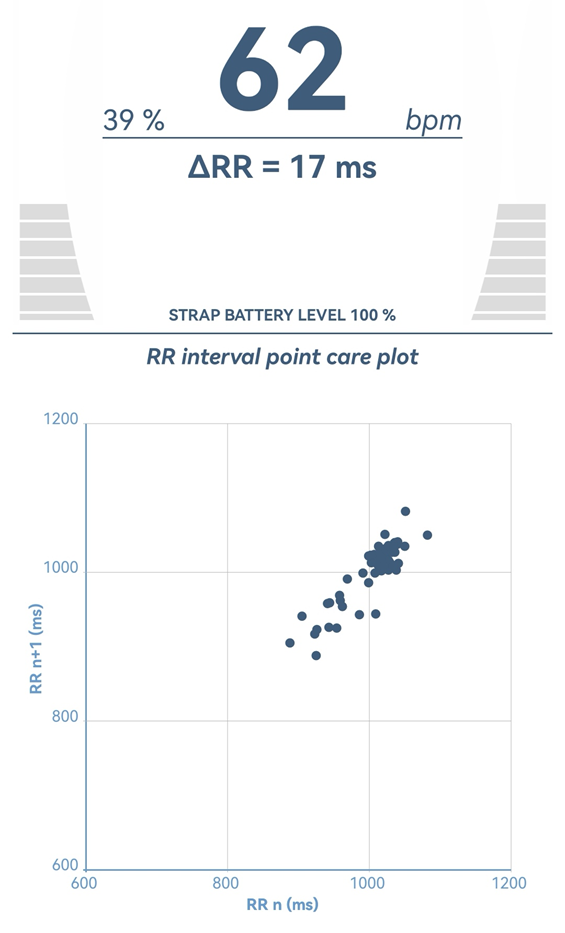
Figure 3A: After Mozart‘s music.
Results
The results obtained in this study are presented in Figure 1, 2, 3, 1A, 2A, 3A.
Discussion
In this study, we observe the relaxing effect of Mozart's classical music. Therefore, we recommend this music to be listened to more often by people to achieve relaxation in their hectic and stressful daily life.
Conclusion
Coordination in young adults, treated or not, must be monitored for life because this pathology must be evoked in front of any hypertension of the young subject associated with a decrease in femoral pulse.
It reflects a global damage to the arterial wall sometimes responsible for long-term aneurysms, dissections and coronary and ventricular sequelae sometimes early.
Early diagnosis prevents the risk of persistent hypertension and especially reduces mortality related to associated complications.
The ESC recommendations detailed in 2020 the management of aortic coarctation in adults [7].
References
- Cyrus Darki, Jennifer Riley, Jennifer Garetto, et al. The Effect of Classical Music on Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Mood, Cureus, 2022; 14(7): e27348. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27348, PMCID: PMC9417331, PMID: 36046316
- Di Cesare M, Tonacci A, Bondi D, Verratti V, Prete G, Malatesta G, et al. Neurovegetative and Emotional Modulation Induced by Mozart’s Music, Neuropsychobiology, 2022; 81: 322–331. https://doi.org/10.1159/000525360
- Parizek D, Sladicekova K, Tonhajzerova I, Veterník, M, Jakus J. "The Effect of Music on Heart Rate Variability (Review)" Acta Medica Martiniana, 2021; 21(1):1-8. https://doi.org/10.2478/acm-2021-0001
- Latha Radhakrishnan, et al. "Effect of music on heart rate variability and stress in medical students." International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Physiology, 2014; 1(2): 131.
- Hans-Joachim Trappe. The effects of music on the cardiovascular system and cardiovascular health. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2010.209858
- Jacquelyn Kulinski, Ernest Kwesi Ofori, Alexis Visotcky, Aaron Smith, Rodney Sparapani, Jerome L Fleg. Effects of music on the cardiovascular system, Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2022; 32(6): Pages 390-398.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2021.06.004.
- Biyun Xue, Jiameng Wang. Effects of Piano Music of Different Tempos on Heart Rate and Autonomic Nervous System During the Recovery Period After High-intensity Exercise, 2022; PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1227474/v1].
- Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation, 1996; 93(5): 1043-10
- Rauscher FH, Shaw GL, Ky KN. Listening to Mozart enhances spatial-temporal reasoning: towards a neurophysiological basis. Neurosci Lett, 1995; 185(1): 44-4
- Roy B, Choudhuri R, Pandey A, Bandopadhyay S, Sarangi S, Kumar Ghatak S. Effect of rotating acoustic stimulus on heart rate variability in healthy adults. Open Neurol J, 2012; 6(1): 71–7
- Sutoo D, Akiyama K. Music improves dopaminergic neurotransmission: demonstration based on the effect of music on blood pressure regulation. Brain Res, 2004; 1016(2): 255–2
- Tan ZY, Ozdemir S, Temiz A, et. al. The effect of relaxing music on heart rate and heart rate variability during ECG Gated-myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Complementary therapies in clinical practice, 2015; 21: 137–140. doi:1016/j.ctcp.2014.12.003.

