Type 3c Diabetes. A New Challenge of 2021 to Diabetologists
Muhammad Arslan1, Mahrukh Ikram2, Rohama Zahid3 and Samreen Riaz4,*
1,2,4 Institute of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan.
3School of Biological Sciences, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
4Pakistan Academy of Family Physician, Pakistan
Received Date: 24/08/2021; Published Date: 17/09/2021
*Corresponding author: Samreen Riaz, Assistant Professor, Institute of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of the Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
Abstract
The patients with chronic pancreatitis or with their pancreas being removed are observed with a high percentage of Diabetes Type 3c, yet they are mostly confused with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Chronic pancreatitis is the leading cause of Type 3c DM along with hemochromatosis and adenocarcinoma etc. The pancreatic tissue abnormality and loss of islet's cells result in the declination in insulin production and hyperglycemic conditions with clinical presentation of abdominal pain, bloating, steatorrhea or maldigestion, and glucose intolerance sometimes in association with PEI. True diagnosis for Type 3c must include pathological pancreatic imaging, and the patient should be checked for PEI as the absence of pancreatic enzyme is another true indicator of type 3c. The DM insulin replacement therapy is preferred for treating Type 3c DM to achieve optimal glucose concentration in blood.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent metabolic disorders in the world; it is characterized by high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) due to the defects in the action of insulin, secretion of insulin or may be due to both of them [80] Type I and Type II diabetes are considered as the major types of diabetes to be known by that time and type II Diabetes is more prevalent (>85%) then that of type I [81] Type I Diabetes is considered to be caused by the deficit insulin secretion from the beta cells of the pancreas that actually happens due to the autoimmune devastation of the beta cells. On the other hand, diabetes type II is caused by two coupled reasons, the first one is the resistance to insulin action, and the second one is the insufficient compensatory insulin secretory response. “Gestational Diabetes mellitus” (GDM), which is also a situation of glucose intolerance, is known to be recognized during pregnancy. Except for these above-mentioned types of Diabetes, there are some more specific categories of diabetes mellitus, and Type 3c Diabetes falls in this category [82].
Among the people suffering from Diabetes mellitus, approximately 2 percent of them have type 3c diabetes [83]. Type 3c diabetes might happen due to genetic and non-genetic factors that comprise pancreatic removal, pancreatitis, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, hemochromatosis, or cystic fibrosis. One of the most dominating causes of Type 3c diabetes is chronic pancreatitis. Unfortunately, patients who have type 3c diabetes are not diagnosed properly and timely, which is one of the main causes of delay in their required treatment [84].
Type 3c Diabetes Mellitus (T3cDM)
Type 3c diabetes mellitus has been designated as secondary diabetes and usually called the pancreatogenic diabetes. One can also develop type 3c if they have a part or all of the pancreases removed because of any other damage. Some people who take steroids can also develop this type of diabetes. This is also called steroid-induced diabetes and is more common in people at high risk of type II diabetes.
Pathogenesis of Type 3c Diabetes mellitus
The declination characterizes the pathogenesis of T3cDM in insulin production that might be due to the reduced number of the islet’s cells or due to the loss of functionality attributed to fibrosis or sclerosis [85]. Basically, the pancreatic tissue damage causes the deficiency of insulin, and its mechanism can be explained by the functionality-dependent interplay between the acinar cells and islets cells.
Pancreatic Function
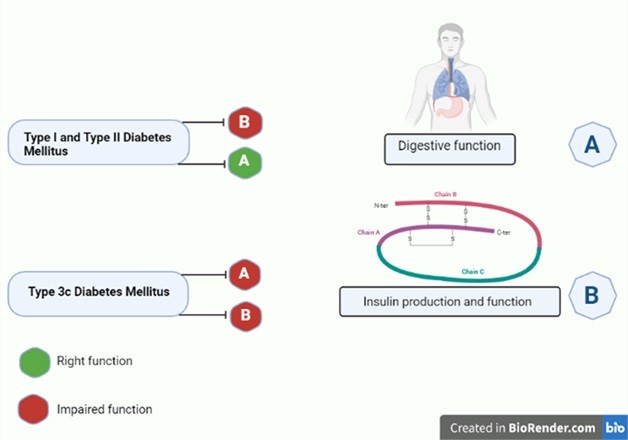
The pancreas holds two significant functions in the human body, firstly, it controls the blood glucose levels, and secondly, it assists in the digestion of the food. Anatomically, the pancreas is divided into five regions associated with the gall bladder, duodenum, and spleen. It has both the exocrine and the endocrine regions. Still, the maximum region of the pancreas owns an exocrine function responsible for the formation and release of the digestive enzymes into the duodenum. Acinar cells that makeup to 85 percent of the pancreatic cells is devoted to synthesizing the enzymes for carbohydrates, lipids, and protein digestion. The main enzyme contributors include amylases, lipases and trypsin, and zymogens (proelastase, trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen procarboxypeptidase). Endocrine secretory tissues residing in the pancreas are called the islets of Langerhans, containing four types of cells. The beta cells (Insulin secreting cells) are in a huge amount. In Type I and Type II Diabetes mellitus, deficient insulin production leads to hyperglycemia, but the digestion of food is unaffected. On the other hand, in Type 3c Diabetes mellitus, digestion of food also gets affected.
Causes of Type3c Diabetes Mellitus
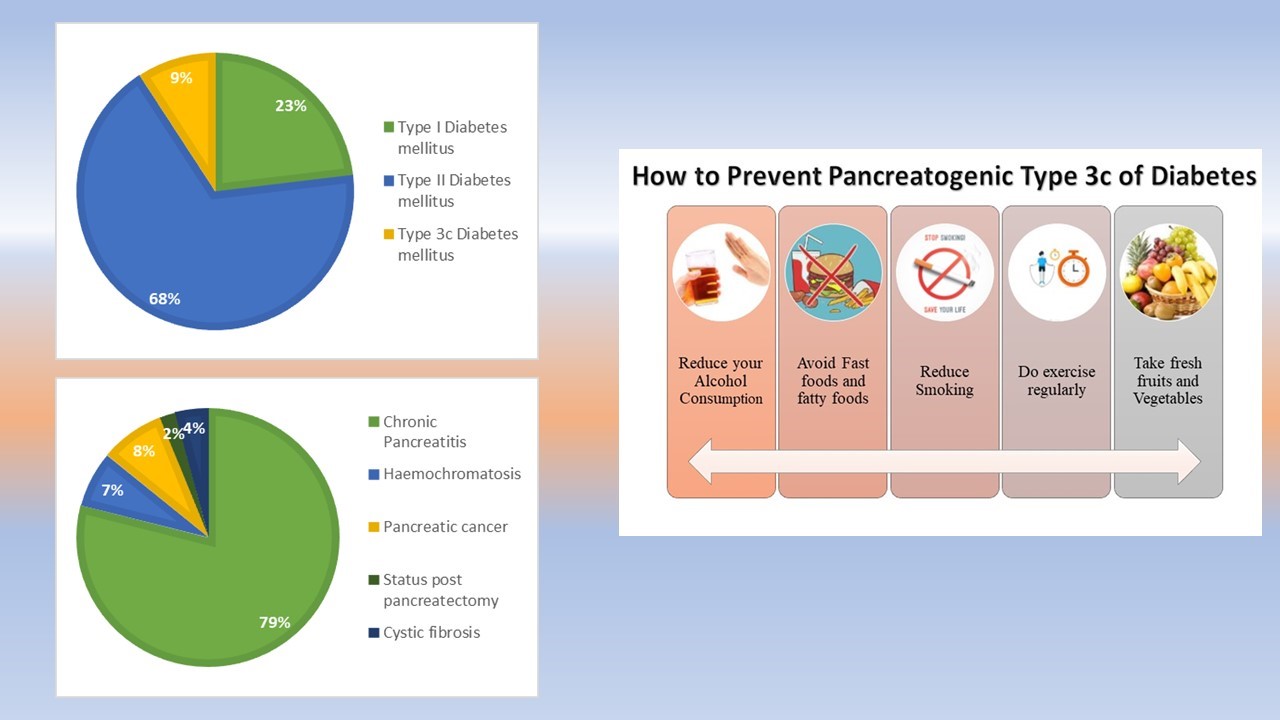
One of the most frequently recognized causes of Type 3c diabetes mellitus is chronic pancreatitis. The most commonly identified cause of type 3c diabetes is chronic pancreatitis. According to a single-center review, causes of type 3c diabetes were recorded as: “chronic pancreatitis” (79%), “pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma” (8%), “hemochromatosis” (7%), “cystic fibrosis” (4%), and previous pancreatectomy (2%), results are also depicted in the Pie Chart. [86]
Chronic Pancreatitis and Type 3c Diabetes mellitus
Progressive inflammation in the pancreatic tissue results in chronic pancreatitis. Genetic and environmental factors are both considered as its cause. It is characterized by the gradual devastation of the pancreatic secretory parenchyma and results in the replacement with the fibrous cells. This condition leads to Diabetes mellitus [87]. On the other hand, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are the triggering factors for pancreatitis; they are the enhancers of inflammation that can convert the impaired acinar cell into a manufactory for the cytokines and chemokines [88]. Such types of inflammatory responses are the instigating factors for the beta-cell disruption and, resultantly, low levels of insulin and hyperglycemic condition [89]. However, there is a lack of systematic studies that can examine the main genetic differences between type 3c diabetes secondary to chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and Type 3c Diabetes mellitus
Pancreatic cancer is the leading cause of wide-scale deaths worldwide, and its risk is high in patients with new-onset diabetes. Therefore, it is named pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC)-associated diabetes mellitus (PDAC-DM), a “type 3C diabetes”. The onset of “PDAC-DM” mostly occurs 2–5 years before diagnosing “PDAC,” which’s why its early diagnosis is very significant. However, it is not possible to differentiate PDAC-DM from other diabetes based on clinical signs and symptoms. There is an urgent need for specific markers in the health sector [90].
Cystic fibrosis and type3c Diabetes mellitus
Cystic fibrosis diabetes is the most apparent form of diabetes in people with cystic fibrosis. Although it possesses characteristics of both type 1 and type 2, it is a quite different condition. Type 3c diabetes develops mainly due to the damage of the pancreas that can happen because of a few typical reasons. Although it is much different from other types, you can still get the wrong diagnosis of diabetes type 2 because Type 3c isn’t well diagnosed. Becoming unable to get the right diagnosis can be tough to deal with it emotionally. You may feel angry for not having the right treatment, or maybe you could just get ruined by the whole process. Thus, make sure you find the right person to communicate with.
Clinical Presentation of Type 3c Diabetes Mellitus:
Many patients suffering from type 3c Diabetes mellitus have some history of pancreatitis along with abdominal pain, steatorrhea, or maldigestion with nutritional deficiencies and glucose intolerance. Patients may also flex the symptoms of maldigestion or abdominal pain without any diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis, or even maybe asymptomatic except for glucose intolerance. Only through careful clinical evaluation is pancreatic disease suspected [91].
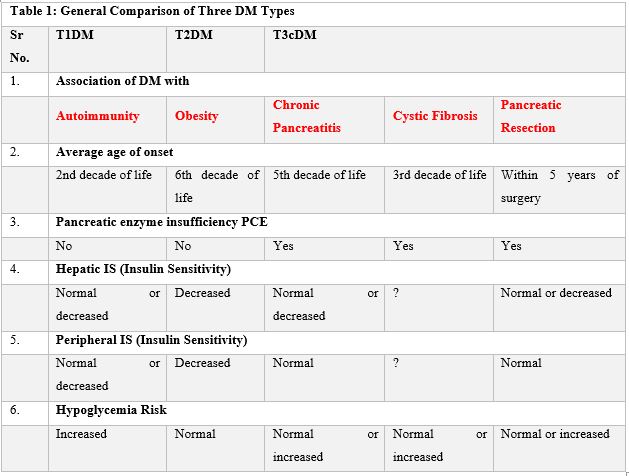
Table 1: General Comparison of Three DM Types.
Symptoms of Diabetes Type 3c
Diabetes type 3c is a complex situation in which this is very difficult to diagnose the problem. In specific, several symptoms are associated with PEI (Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency). In this disease, the pancreas is not functional anymore, and it does not provide the body with the essential enzymes required for appropriate digestion. This is mainly due to chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. That is the reason why the symptoms of Diabetes type 3c are usually linked with digestive tract symptoms. The major symptoms include [72]:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal bloating
- Eating issues
- Bloating and abdominal pain
- Nausea
- General fatigue
These symptoms are usually accompanied by several conditions like patients with a history of pancreatic disorders, an instance of weight loss, and severe pain. [73]
Diagnosis of Diabetes Type 3c
Diagnosis of Diabetes type 3c is too complicated, and that’s why it renders it undiagnosed and maltreated in most cases. A few reasons for its being difficult to diagnose are the high variability of glucose levels in the blood, i.e., it sometimes becomes too high and sometimes too low. That's why it sometimes sounds like Diabetes type 1 and hyperglycemia, and sometimes it seems to be hyperglycemic. Now, after a long run of research, there has been set a few standard steps to follow when diagnosing for Diabetes [73] which are:
1. Check for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
2. Perform pathological pancreatic imaging
3. Check for Diabetes type 1-associated auto-antibodies
Based on these criteria, there can be several ways to check for type 3c and rule out the other types; for example, the absence of pancreatic enzymes in the body after glucose or mixed meal can be a true sign of type 3c. [73] HbA1C was initially thought to be a screening test for DM type 3c, but there is a much lower connection between A1c and insulin tolerance levels. That’s why HbA1c can’t be used as a standard technique to diagnose DM type 3c [76]. It is simply conclusive that the major relation of diabetes type 3c is with PEI and pancreatic disorders, so diagnosing in-depth for the problems associated with pancreatic problems is the major gateway to diagnose type 3c [74].
General overview of the differential criteria between T2 and T3c DM
Type 3c is characterized by a deficiency of PP (pancreatic polypeptide), whereas type 2 contains high levels of nutrient-stimulated pancreatic polypeptide, i.e., PP. Different criteria on which Type 2 DM and Type 3c DM can be categorized, including pathological imagining, i.e., endoscopy, MRI and ultrasound, etc. The absence of some autoimmune markers associated with Type 1 DM is another basis of differentiation between these two. Some minor criteria include identifying B-cell functionality, IR (Insulin Resistance), Abnormalities of incretin secretion, and low levels of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). However, Type 3c and Type 2 DM still overlap at many points, which will need more research to differentiate the different types of diabetes [79].
Management of Diabetes Type 3c
Management of Diabetes type 3c is not a much-researched field due to fewer reported and diagnosed cases [76]. Management is based upon the cause of particular type 3c diabetes. Usually, it is suggested that the patients get some knowledge and awareness about diabetes management in sessions about the diabetes awareness programs and seminars [76]. The basic need is to maintain a little greater than the normal level of glucose in the body, i.e., to avoid hypoglycemia [78]. On the other hand, it is suggested that patients with a history of chronic pancreatitis take a rich diet in dietary fiber and lack fat. In this way, they can avoid the symptoms of steatorrhea, and they must also need to prevent hyperglycemia through diet. [78] Thus, it can be said that the only way to manage this least researched form of diabetes is to use a multi-dimensional approach in which both nutritional and therapeutic parameters are taken underuse. [77] And to minimize the serious complications, strategic management should be balanced to maintain maximum glycemic control. Other healthy improvisions can also be helpful to prevent hyperglycemia [78].
Treatment of Diabetes Type 3c
About 75% of type 3c diabetes result from chronic pancreatitis, which ultimately increases the risk of the development of carcinoma in the pancreas. Treatment with insulin or insulin secretagogue can readily increase the risk of malignancy due to their hypoglycemic activity, whereas metformin could be beneficial in reducing it. However, in advanced type 3c, DM insulin replacement therapy is preferred, which helps the patients achieve optimal glucose concentration in blood by mimicking the physiological delivery of insulin in a very comprehensive approach.[79].
Conclusion
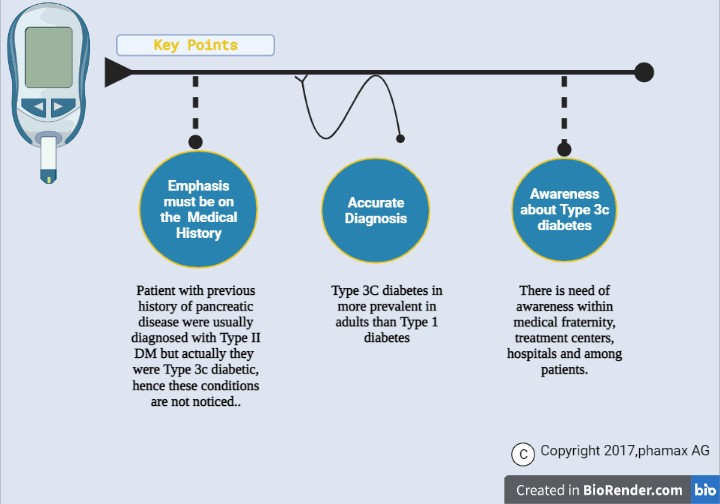
Type 3c DM is getting prevalent today due to a lack of diagnostic sense in the people as it is always confused with Diabetes type 1 and type 2. Type 3c DM is majorly caused by chronic pancreatitis, adenocarcinoma, hemochromatosis, or pancreatic removal. So, patients with these problems should be identified in their medical histories and distinguished from other diabetic patients.
Conclusion
The authors declare that the publication of this article has no conflict of interest.
References
- Riaz S, Mughal MS. Histopathological changes in kidney of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella as manifested by chromium intoxication. Biologia, 2000; 46(1&2): 83-88.
- Riaz S, Mughal MS. Histopathological changes in spleen of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella as manifested by chromium intoxication. Biologia, 2002; 48(1&2): 401-405.
- Riaz S, Mughal MS. Effect of different levels of tannery wastes on serum enzymes of quail chicks Coturnix coturnix japonica. Biologia, 2002; 48(1&2): 389-400.
- Riaz S, Mughal MS. Histopathological changes of different levels of tannery wastes replaced by chrome shavings in liver & kidney of quail chicks Coturnix coturnix japonica. Biologia, 2002; 48(1&2): 341-349.
- Riaz S, Riaz A. Effect of different levels of chrome shaving, 2006.
- Riaz S, Shoukat S, Mughal MS. Fluoride toxicity, 2007.
- Riaz S, Shoukat S, Mughal MS. Fluoride toxicity on the histopathological aspects of kidney in the Cirrhinus mrigala. Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2008; 40(3): pp20-24.
- Riaz S, Alam SS, Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ, Aktar MW. Proteomic strategies to study the protein biomarker for diabetes mellitus and effect of thiamine on their levels. Proceeding of Symposium of Genomics, Proteomics and Metabolomics. Modern trends in biotechnology. Dept. of MMG, University of the Punjab, Lahore. 2009; p198-212.
- Riaz S, Alam SS, Ikram A. Histopathological changes observed in the heart and gizzard of quail chicks Coturnix coturnix japonica administrated by the different levels of chrome shaving. African Journal of Biotechnology 2006; 5(19): p. 1765-1769.
- Riaz S, Alam SS. Evaluation of nutritive value of different levels of chrome shaving partially replacing animal protein in the feed on the performance of quail chicks. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 2006; 1(1): pp.1-7.
- Riaz S, Alam SS, Ali G. Effect of different levels of chrome shavings on hematological parameters in the blood of quail chicks. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 2006; 1(1): pp.27-32.
- Naila Rabbani, Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, James Larkin, M Waheed Akhtar, Tahir Shafi, Paul J Thornalley. High dose thiamine therapy for people with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. 2009; 52(2): 208-212.
- Samreen Riaz, Mehreen Raza, Saadia Shhazad Alam, Shahida Hasnain, Waheed Akhtar M. Obesity as risk factor and study of obesity related proteins in diabetes mellitus. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2009; 8(5): pp. 737-744.
- Nawaz K, Riaz S, Riaz S, Hasnain S. Screening of anti-Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteriocin Producing Bacteria. African Journal of Biotechnology. 2009; 8(3): pp. 365-368.
- Rabbani N, Shahzad Alam S, Riaz S, Larkin JR, Akhtar MW, Shafi T, et al. Response to comment on Rabbani, et al. High dose thiamine therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a pilot randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia, 2009; 52(2): 208-212, Diabetologia. 2009; 52(6): 1214-1216.
- Diabetes: Could vitamin 'B' the answer? Chloë Harman Comments on Original article, Naila Rabbani, Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, James Larkin, M Waheed Akhtar, Tahir Shafi, et al. High dose thiamine therapy for people with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 208–212. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2009; 5(5): 236-236. Research Highlights.
- Diabetes: Could vitamin 'B' the answer? Chloë Harman Comments on Original article, Naila Rabbani, Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, James Larkin, M Waheed Akhtar, Tahir Shafi and Paul J Thornalley. High dose thiamine therapy for people with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 208-212. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2009; 5(4): 182.
- Samreen Riaz, Diabetes mellitus (Review article) Scientific Research and Essay. 2009; 4(5): pp. 367-373.
- Samreen Riaz, Saadia Shahzad Alam, Waheed Akhtar M. Proteomic Identification of human serum biomarkers in diabetes mellitus type-2. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2010; 51(5): 1103-1107.
- Samreen Riaz and Ansa Butt. Study of Protein profiling of human urine in diabetic hypertensive nephropathy versus normal healthy controls. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics. 2010; 12(5): 379-386.
- Samreen Riaz, Saadia Shahzad Alam, Surjit Kaila Srai, Vernon Skinner, Aasma Riaz, Waheed Akhtar. Proteomic Identification of human urine biomarkers in diabetes mellitus type-2. Journal of Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics. 2010; 12(12): 979- 988.
- Samreen Riaz, Vernon Skinner, Surjit Kaila Srai. Effect of high dose thiamine on levels of human urine protein biomarkers in diabetes mellitus type 2. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2011; 54(4): 817-825.
- Samreen Riaz, Vernon Skinner, Surjit Kaila Srai. Corrigendum to “Effect of high dose thiamine on the levels of urinary protein biomarkers in diabetes mellitus type 2” [J. Pharm. biomed. Anal. 2011; 54: 817–825, Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2011; 56(1): 139.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of high dose thiamine therapy on activity and molecular aspects of transketolase in Type 2 diabetic patients. African Journal of Biotechnology 2011; 10(75): p. 17305-17316.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of High Dose Thiamine Therapy on Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetics. Journal of Diabetes and Metabolism 2012; 3: 10.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of high dose thiamine therapy on induction and activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in type 1 diabetic patients. British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research. 2013; 12(10): 1-12.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of high dose thiamine therapy on activity and molecular aspects of transketolase in Type 1 diabetic patients. African Journal of Biotechnology 2013; 12(75): p. 17305-17316.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of high dose thiamine therapy on induction and activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics. 2013; 12(12): 979-988.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz, Waheed Akhtar M. Effect of high dose thiamine therapy on induction and activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Educator. 2013; 12(1): pp. 1-15.
- Samreen Riaz and Sadia Rana. Analysis of uropathogenes among type II diabetic patients in Pakistani population. Diabetes and Metabolism, 2014; 2(2): pp. 31-41.
- Samreen Riaz. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Diabetes Mellitus in the Local Population of Pakistan. Universal Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2014; 2(3): p. 58–64.
- Samreen Riaz. Evaluation and Analysis of Human Folate levels in Pakistani diabetic Population. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research (IJSER), 2014; 5(12): p. 1572-1576.
- Samreen Riaz. Study of protein biomarkers of diabetes mellitus type 2 and therapy with Vitamin B1. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. Journal of Diabetes Research. 2015; 2015: pp. 1-10.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz. Induction and activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in type 2 diabetic patients and therapy with Vitamin B1. International Journal of advances in Medicine and Medical Research. 2016; 12(10): pp.1-10.
- Taher Mursleen, Samreen Riaz. Implication of homocysteine in diabetes and impact of folate and vitamin B12 in diabetic population. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews November issue Special, 2017; S141–S146.
- Riaz S. Therapeutic Implication of Folate-Homocysteine Interaction in the Local Diabetic Pakistani Population. Vascular Medicine 2018; 5(1): 1085-1089.
- Afifa, Samreen Riaz. Analysis of Pyridoxine in the Male Diabetic Population of Lahore and Sheikhupura. Annals of Diabetes Metabolic Disorders & Control. 2018; 2(1): 118.
- Riaz S, Tariq M. Linkage of Micro Albuminuria and Serum Albumin Levels in the Diabetic Patients Punjab University Premises. Annals of Diabetes Metabolic Disorders & Control, 2018; 2(1): 117.
- Riaz S, Tariq M, Aslam S. Association of Serum Protein Levels in the Diabetic Patients with Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Nephropathy in Pakistani Population. Diabetes and Metabolism Journal. 2018; 4(1): 011-015.
- Afifa, Samreen Riaz. Analysis of Pyridoxine in the Male Diabetic Population of Lahore and Sheikhupura. Annals of Diabetes Metabolic Disorders & Control. 2018; 2(1): 118.
- Haseeba Yousaf, Samreen Riaz. Biomolecular Evaluation of Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) in the Diabetic Population of Lahore and Sheikhupura. Annals of Diabetes Metabolic Disorders & Control. 2018; 2(1): 119.
- Samreen Riaz, Shagufta Naz, Umera kousar, Zil E Huma Malik, Rasheeda Bashir. Major Complication Associated with Diabetes Mellitus Type II in Punjab and Khyber Paktunkhwa Population. Research Article: Diabetes and Metabolism, 2018; 9: 809.
- Javaria yasin, Samreen Raiz. "Evolutionary history and molecular epidemiology of HIV pol gene in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences. 2019; 15(1); 1-10.
- Samreen Riaz, and Amina Mehboob (2020). Olive oil tends to lowers cholesterol level in patients suffering from diabetes. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 2020; 99154-JBS-ANSI: pp 1-10.
- Nusair Malik, Arwa Faisal, Snobia Munir, Samreen Riaz. Clinical and microbiological profile of urinary tract infection in male diabetic patients. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2020; 8(1): 30‒34.
- Farah Qudsia, Hafiza Amina Matti, Samreen Riaz. Pleiotropic Effect of Folate-Cobalamin Combinational Therapy on Diabetes Mellitus. Annals of Nutrition Disorders and Therapy. 2020; 7(1): 1061.
- Snobia Munir, Samreen Riaz. Type 2 diabetes and cancer. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2020; 4: 001-006.
- Snobia Munir, Samreen Riaz. Molecular Association of Diabetes Mellitus with Different types of Cancer from Population of Lahore. Annals of Diabetes, Metabolic Disorders and Control. 2020; 3(1): 126.
- Hafiza Amina Matti, Samreen Riaz. Molecular Association of Cancer and Diabetes Mellitus with Combinational Therapy. International European Extended Enablement in Science, Engineering & Management (IEEE-SEM), 2020; 8(4).
- Hafiza Amina Matti, Samreen Riaz. Evaluation of Environmental Influence of Arsenic Compounds on Patients Suffering from Type 2 Diabetes. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research (IJSER), 2020.
- Samreen Riaz, Shagufta Naz, Umera kousar, Zil E Huma Malik, Rasheeda Bashir. The association between VEGF rs699947 polymorphism and their serum level in patients with diabetic foot ulcer in Pakistani population, 2020.
- Samreen Riaz and Abdullah Mohsin, (2020). Role of Phytochemicals Derived from Plants Biodiversity and its Impact in Treating COVID-19. Journal of Bioscience & Biongineering. 2020; 1(3): Pp. 1-8.
- Nusair Malik, Muhammad Suhail, Muhammad Zubair, Samreen Riaz. Therapeutic interventions of EVOO as neutraceutical agent to lower lipid profile in the diabetes mellitus type 2. Journal of Bioscience & Biongineering, 2020; 1(3): p. 1-8.
- Munir S, Riaz S, Arshad T, Riaz A. Risk Factors Associated to Patients with Type 2Diabetes in Lahore District. Annals of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2020; 4: 011-019.
- Samreen Riaz. Molecular Association of Coronavirus with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 in Pakistan Journal of Diabetes Research. 2020; 2(4): 1-11.
- Areeba Saeed, Sohaib Imtiaz and Samreen Riaz. Study of Urinary tract infection in female patients suffering from cancer. Journal of Cancer Research Reviews & Reports. 2020; 2(2): p.1-15.
- Sohaib Imtiaz, Samreen Riaz. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of bacteria isolated from male cancer patients. International Journal of Clinical Studies & Medical Case Reports. 2020; 6(3): p. 1-6.
- Samreen Riaz, Shakeeb ul Arsalan, Rajab Ali, Asma Riaz. Statistical Analysis to Identify the Effect of Risk Factors on Diabetic Patients from the Sheikh Zayed Hospital Lahore. Current Trends on Biostatistics and Biometrics. 3(3); p. 368-382.
- Riffat Iqbal, Shaista Aslam, Irum Liaqat ,Aneeqa Zafar, Kiran Aftab and Samreen Riaz, Polymorphisms in CDKN2B-AS1 gene Confer a Risk for Myocardial Infarction in Pakistani Population. Bioscience Reports. BSR 2021-2003.
- Saima Shokat, Riffat Iqbal, Atif Yaqub, Fatima Shahid and Samreen Riaz. Analysis of environmental Pollutants as Diabetogenic Agent in the Patient Suffering from Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes & Obesity International Journal. 2021; 6(1).
- Samreen Riaz, Abdullah Mohsin, Saima Shokat, and Saba Shamim. Molecular Level Microbiological and Clinical Profile of Urinary Tract Infection in Diabetes Mellitus, Journal of Microbiology, 2021.
- Fizza Sikander and Samreen Riaz (2021). Intestinal Cancer and role of Phytochemicals. International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research(IJSER) - (ISSN 2229-5518). IJSER 2021; 12(1).
- Samreen Riaz. Type 3c Diabetes. A New Challenge 2021 to Diabetologist, 2021.
- Noor Fatima Shahid, Saima Shokat, Samreen Riaz. Coronoa Virus Pandemic: New Environmental Pollutant. 2021.
Chapters in Books:
- Samreen Riaz, “Study of Protein Biomarkers for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Role of High Dose Thiamine on their Level” chapter in Book “Advances in Medicine and Biology” (2010). Editor, Leon V Berhardt. Book Hauppauge, N.Y. 11788-3619, USA. Phone (631) 231-7269 * Fax (631) 299-0165. http://www.novapublishers.com. I:\Nova publishs\Advances in Medicine and Biology_Volume 13.htm.Chapter 11. Volume 13. page numbers. 163-176. Nova Science Publishers, Inc. 400 Oser Avenue, Suite 1600.
- Samreen Riaz, Saadia Shahzad Alam. STUDY OF DIABETIC HYPERTENSIVE NEPHROPATHY IN THE LOCAL POPULATION OF PAKISTAN. chapter in Book “Diabetic Nephropathy”, Book edited by: Prof. Dr. John S.D. Chan. Ph.D, Professor of Medicine/Professeur sous octroi titulaire, Faculty of Medicine/Faculté de médecine, Université de Montréal, Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Nephrology and Endocrinology, CRCHUM- Hôtel-Dieu Hôpital Montréal, Québec, Canada. ISBN 978-953-308-11-6, 2012.
- Samreen Riaz. Protein Biomarkers for diabetes mellitus type 2 chapter in Book: “Biomarker”. edited by: Assoc. Prof. Tapan Kumar Khan, Blanchette Rockefeller Neurosciences Institute at West Virginia University, USA. ISBN 979-953-307-612-5. In tech Publishers. USA, 2013.
- Saadia Shahzad Alam, Samreen Riaz. Thiamine and the Cellular Energy Cycles — A Novel Perspective on Type 2 Diabetes Treatment, chapter in Book “Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes”, Colleen Croniger (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-2032-2, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/59224. 2015; Chapter 2 page 23-59.
- Samreen Riaz. THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATION OF FOLATE-HOMOCYSTEINE INTERACTION IN THE LOCAL DIABETIC POPULATION. FOLATE. Chapter in Book “FOLATE” ISBN 978-953-51-6191-2 Book edited by: Dr. Jean Guy LeBlan, 2018.
- Riaz S. Biomolecular Analysis of serum Albumin and Microalbuminuria in the Diabetic patients of Punjab University Premises. Chapter in book. “Top ten Contributors on Diabetes”. Chapter 6. Avid Science Publishers. 2018; Pp 1-18.
- Samreen Riaz, Muhamamd Suhail. In-Silico Proteomics EVOO therapy for lipid lowering in the Patients of Diabetes Mellitus. Chapter in Book “Biochemical Testing - Fundamentals of Medical & Laboratory Science" Intech Open Science Publishers USA, 2019-2020; PP 1-25.
- Johnson CD, Arbuckle R, Bonner N, Connett G, Dominguez-Munoz E, Levy P, et al. Qualitative assessment of the symptoms and impact of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) to inform the development of a Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) instrument. The Patient-Patient-Centered Outcomes Research, 2017; 10(5): 615-628.
- Conlon KC, Duggan SN. Pancreatogenic type 3c diabetes: underestimated, underappreciated and poorly managed. Practical gastroenterology, 2017; 15.
- Ewald N, Kaufmann C, Raspe A, Kloer HU, Bretzel RG, Hardt PD. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews, 2012; 28(4): 338-342.
- Ewald N, Kaufmann C, Raspe A, Kloer HU, Bretzel RG, Hardt PD. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes, 2007; 115(S1): P01_028.
- Moran A, Brunzell C, Cohen RC, Katz M, Marshall BC, Onady G, et al. Clinical care guidelines for cystic fibrosis–related diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and a clinical practice guideline of the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, endorsed by the Pediatric Endocrine Society. Diabetes care, 2010; 33(12): 2697-2708.
- Rickels MR, Bellin M, Toledo FG, Robertson RP, Andersen DK, Chari ST, et al. Detection, evaluation and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis: recommendations from Pancreas Fest 2012. Pancreatology, 2013; 13(4): 336-342.
- Makuc J. Management of pancreatogenic diabetes: challenges and solutions. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity: targets and therapy, 2016; 9: 311.
- Andersen DK, Andren-Sandberg Å, Duell EJ, Goggins M, Korc M, Petersen GM, et al. Pancreatitis-diabetes-pancreatic cancer: summary of an NIDDK-NCI workshop. Pancreas, 2013; 42(8).
- Golden SH, Robinson KA, Saldanha I, Anton B, Ladenson PW. Prevalence and incidence of endocrine and metabolic disorders in the United States: a comprehensive review. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2009; 94(6): 1853-1878.
- Forouhi, N. G., & Wareham, N. J. (2010). Epidemiology of diabetes. Medicine, 2010; 38(11): 602-606.
- Mellitus D. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes care, 2005; 28(S37): S5-S10.
- Liu QC, Zhuang ZH, Zeng K, Cheng ZJ, Gao F, Wang ZQ. Prevalence of pancreatic diabetes in patients carrying mutations or polymorphisms of the PRSS1 gene in the Han population. Diabetes technology & therapeutics, 2009; 11(12): 799-804.
- Hart PA, Bellin MD, Andersen DK, Bradley D, Cruz-Monserrate Z, Forsmark CE, et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. The lancet Gastroenterology & hepatology, 2016; 1(3): 226-237.
- Domschke S, Stock KP, Pichl J, Schneider MU, Domschke W. Beta-cell reserve capacity in chronic pancreatitis. Hepato-gastroenterology, 1985; 32(1): 27-30.
- Ewald N, Kaufmann C, Raspe A, Kloer HU, Bretzel RG, Hardt PD. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c). Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews, 2012; 28(4): 338-342.
- Sarles H. Etiopathogenesis and definition of chronic pancreatitis. Digestive diseases and sciences, 1986; 31(9): 91-107.
- Braganza JM, Lee SH, McCloy RF, McMahon MJ. Chronic pancreatitis. The Lancet, 2011; 377(9772): 1184-1197.
- Sasikala M, Talukdar R, Radhika G, Rao GV, Pradeep R, Subramanyam C, et al. β-Cell dysfunction in chronic pancreatitis. Digestive diseases and sciences, 2012; 57(7): 1764-1772.
- Gao W, Zhou Y, Li Q, Zhou Q, Tan L, Song Y, et al. Analysis of global gene expression profiles suggests a role of acute inflammation in type 3C diabetes mellitus caused by pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Diabetologia, 2015; 58(4): 835-844.
- Gudipaty L, Rickels MR. Pancreatogenic (type 3c) diabetes. Pancreapedia: The Exocrine Pancreas Knowledge Base, 2015.

