Congenital Syphilis, Rare Presentation and Unpredictable Progression
Fajri Zineb, Hanane Baybay, Meryem Soughi, Zakia Douhi, Sara Elloudi, Fatima Zahra Mernissi
Department of Dermatology, Hassan University Hospital Center II, Morocco
Received Date: 07/03/2024; Published Date: 17/07/2024
*Corresponding author: Fajri Zineb, Department of Medicine, Hassan University Hospital Center II, Morocco
Introduction
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which belongs to the Treponemataceae family. Congenital syphilis (CS) resulting from vertical transmission of Treponema pallidum during early pregnancy [1] can be detrimental to the health of the foetus, with unpredictable consequences. Diagnosing CS and the therapeutic course can be challenging [2]. Maternal management is based on early administration of penicillin, and infant management is based on diagnosis and early treatment with parenteral penicillin [3]. Screening and treatment of syphilis in pregnant women remains the best way to prevent the congenital form of the disease.
Case Report
A newborn, from a non-consanguineous marriage, from an unattended pregnancy, carried to term, was born with a 3 kg birthweight via spontaneous vaginal delivery, to a 30-year-old primigravida mother with no pregnancy follow-up, consulted in the neonatology department for lesions on the palmoplantar area, in the context of a fever, the general examination finds a febrile nourishing at 38, icteric and hypotonic, the dermatological examination objectifies multiple flaccid bullae at the plantar and palmar and at the dorsal of the hands (Figure A).
The clinical examination was suggesting early congenital syphilis especially since the pregnancy was not followed. The complete blood count showed an anemia (11 mmol/L) and thrombocytopenia (118 103/uL) with elevated leucocytes (14.81 103/uL), CRP (90 mg/L) and positive syphilis serology. The mother's blood test showed positive treponemal results with TPHA=1/1280, VDRL= 1/16. The lumbar puncture was normal, and X-rays of the long bones showed periosteal reaction and osteochondritis of the ulna and radius (Figure B), the hepatic function was affected with hepatic cytolysis.
The diagnosis of neonatal syphilis with osteoarticular involvement but no neurological involvement is retained. The patient was admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit, after consultation with the pediatricians, we started her on ampicillin for 10 days, since penicillin G IV was not available. The evolution was marked with disappearance of the skin lesions, but exacerbation of icterus, hepatosplenomegaly with abdominal distension and haemodynamic and respiratory instability. Hypotensive, tachycardia to 160, polypnoea to 80, Sao2 to 70%, hypertension, the infant died of sepsis.
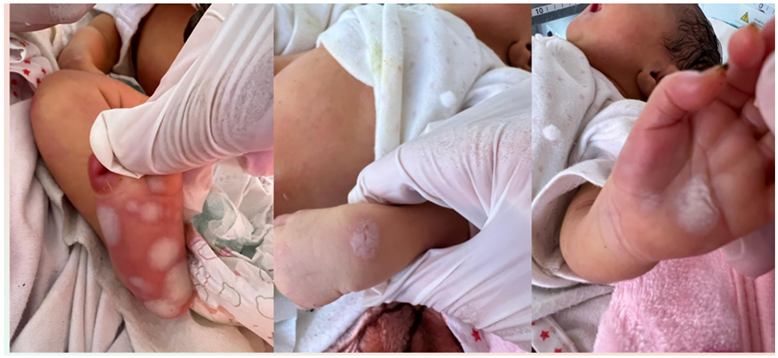
Figure A: Multiple flaccid bullae at the plantar and palmar and at the dorsal of the hands.
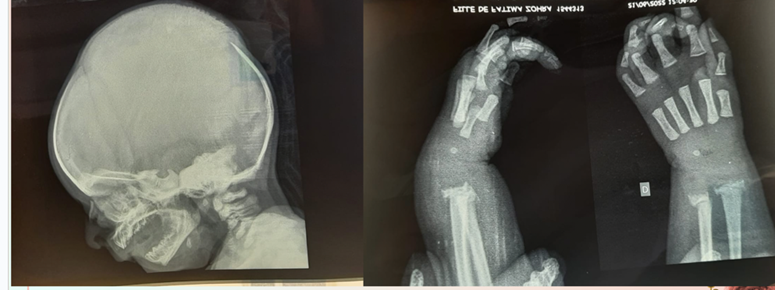
Figure B: X-rays of the long bones showed periosteal reaction, osteochondritis of the ulna and radius.
Sepsis and multivisceral deficiency, we also treated the mother, after a normal clinical examination, we requested a syphilis serology from the father, who refused.
Discussion
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted contamination caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum, invasive bacterium able to crossing the placental barrier, main to congenital syphilis from an inflamed mom at some stage in any Stade of a pregnancy. Congenital syphilis is a first-rate public health problem in developing countries, but also inside the West in populations where there's little or no tracking of pregnant ladies [2]. The occurrence of congenital syphilis seems to be reducing in several international locations with the introduction of preventive prenatal screening advocated by way of the WHO, all through being pregnant, its miles related to premature delivery, spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, nonimmune hydrops, perinatal dying [3]. CS is split into early and late ailment primarily based on consequences that seem earlier than or after the age of two years. Early CS is typically present in the neo-natal period within the first four to 8 weeks. more than half (60–90%) of liveborn babies are asymptomatic at beginning, with first clinical signs supplying with the aid of the age of 3 months [4]. Mucocutaneous lesions are outstanding manifestations that arise in 40–60%, it manifests with the aid of a maculopapular rash which turns into copper-colored with desquamation basically inside the hands and soles, a bullous rash known as syphilitic pemphigus might also expand with peeling and in all likelihood scabs and wrinkles within the pores and skin. Rhinitis (“snuffles”), a nasal discharge that is first of all watery however may come to be thick, purulent, and blood tinged. rarely, cracking of the lips covered with scabs, plaques of the tongue and palate as well as white, flat, moist, raised patches known as condylomata lata inside the perioral and perianal regions [5]. different medical findings may additionally consist of hepatomegaly lymphadenopathy, pneumonia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, osteochondritis, and pseudoparalysis [2]. Ocular findings (chorioretinitis, cataract, glaucoma, and uveitis), gastrointestinal tract leading to malabsorption and diarrhea. The prognosis of congenital syphilis is mounted by means of the commentary of spirochetes in frame fluids or tissue and cautioned by using serologic take a look at consequences Non treponemal testing must be carried out on all babies with suspected CS and ought to involve the identical nontreponemal take a look at completed on the mom for direct assessment. A 4-fold difference inside the mom as opposed to toddler titers is suggestive of CS [2]. mind damage is observed in 50% of likely or showed instances of congenital syphilis, justifying the systematic overall performance of LP. on this context, on the lookout for a neuro syphilis [3], techniques and definitions tend to vary across the world. some countries rely upon a 4-fold boom in IgM titers to diagnose congenital syphilis [5]. The remedy is based on penicillin G Intra-venous 150,000 U/kg/day (in 6 doses each 4 hours) for 10 days (14 days if neurosyphilis) [3]. studies efforts are urgently needed to investigate whether or not different antibiotics inclusive of ampicillin can effectively treat congenital syphilis on kids with history of penicillin allergic reaction or in international locations wherein penis G is not available, currently, there has been an acute scarcity of penicillin.
Conclusion
Congenital syphilis is a severe infection which can have serious consequences on infants and children, it is effectively prevented by prenatal serologic screening of mothers and penicillin treatment of infected women, their sexual partners, and their newborn. Through this case we insist on the importance of serological screening in the mother during pregnancy, for the prevention of severe forms of congenital syphilis, the development of which is unpredictable.
References
- Bezerra MLMB, Fernandes FECV, de Oliveira Nunes JP, de Araújo Baltar SLSM, Randau KP. Congenital Syphilis as a Measure of Maternal and Child Healthcare, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis, 2019; 25: 1469-1476.
- Kwak J, Lamprecht C. A review of the guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of congenital syphilis. Pediatr Ann, 2015; 44: e108-e114.
- Arrieta AC, Singh J. Congenital Syphilis. N Engl J Med, 2019; 381: 2157.
- Keuning MW, Kamp GA, Schonenberg-Meinema D, Dorigo-Zetsma JW, van Zuiden JM, Pajkrt D. Congenital syphilis, the great imitator-case report and review. Lancet Infect Dis, 2020; 20: e173-e179.
- Cooper JM, Sánchez PJ. Congenital syphilis. Semin Perinatol, 2018; 42:176-184.
- Agarwal A, Kumar J. Congenital Syphilis Resurgences and Penicillin Shortage. Indian J Pediatr, 2020; 87: 959-960.
- O’Connor NP, Gonzalez BE, Esper FP, Tamburro J, Kadkhoda K, Foster CB. Congenital syphilis: Missed opportunities and the case for rescreening during pregnancy and at delivery. IDCases, 2020; 22: e00964.

