Diagnosis of Prérupture Pregnancy in the Rudimentary Horn of a Pseudounicornuate Uterus
Etber A, Cherradi S, Slaoui A, Zeraidi N and Baidada A
Department Gynecology-obstétrics and endoscopy, Maternity souissi/university hospital center IBN SINA, Morocco
Received Date: 03/10/2022; Published Date: 26/10/2022
*Corresponding author: Etber Amina, Department Gynecology-obstétrics and endoscopy, Maternity souissi/university hospital center IBN SINA, Rabat, Morocco
Abstract
Pregnancy in the rudimentary horn of a unicornuate uterus is extremely rare. However, its occurrence is serious and can involve the vital maternal pc; in 80 to 90% of cases, the natural evolution of the rudimentary gravid horn is the rupture, frequently occurring in the 2nd trimester. Its diagnosis is not easy, posed late at the stage of rupture in 50% of cases.
Through our case of pregnancy in a rudimentary horn of pseudounicornuate uterus, we report the seriousness of this ectopic pregnancy, its diagnostic difficulties and its therapeutic implications.
Introduction
Unicornuate uterus is a congenital uterine malformation with a prevalence of 0.1%-0.4% in the general population (2.17 ,18,21). The true unicornuate uterus is defined by the presence of a single hemiuterus. The presence of an associated rudimentary horn defines the pseudounicornuate uterus; it is the rudimentary contralateral hemiuterus because of an incomplete development of the corresponding muller duct.
An ectopic pregnancy, in the presence of a cavity and a functional endometrium, can occur in this rudimentary horn.
Case Report
25-year-old patient with no significant medical and surgical history.
Gestality: 2 parities: 1, a live child delivered vaginally at term. The 2nd pregnancy is without clinical particularity. The patient benefited from her 1st trimester ultrasound having objectified a non-evolving monofetal pregnancy of 12 weeks, ectopic; abdominal or tubal location with absence of peritoneal effusion. The surprise diagnosis of a pregnancy on a rudimentary horn was established by MRI. The patient underwent rudimentary horn resection with ipsilateral salpingectomy.
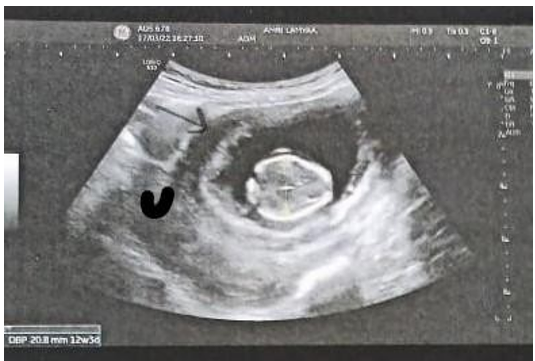
Figure 1: U: uterus, → musculature of rudimentary horn surrounding the gestational sac.
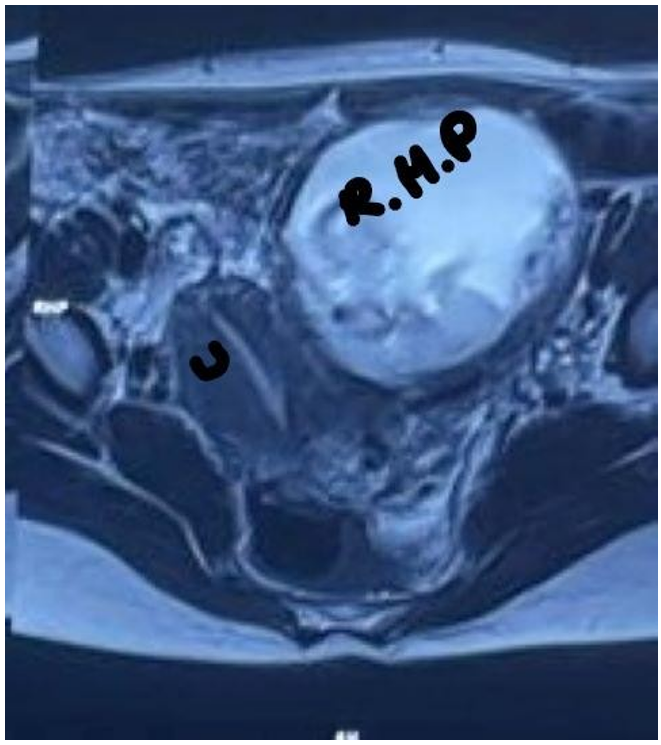
Figure 2: IRM: U: uterus, R.H.P: rudimentary horn pregnancy, myometrial tissue surrounding gestational sac.

Figure 3: IRM: absent visual continuity between the cervical canal and the lumen of the pregnant horn.
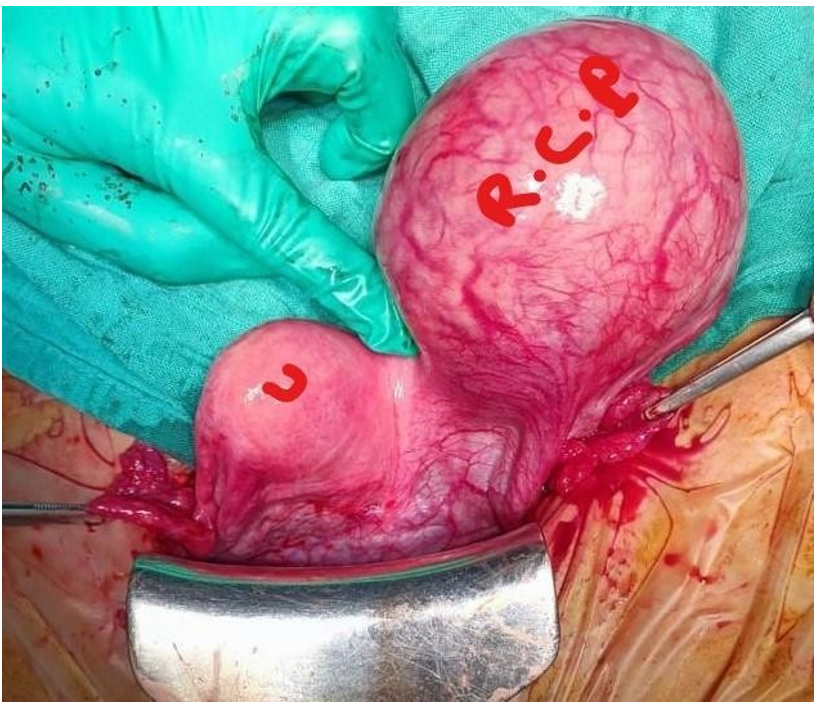
Figure 4: Shows uterus (U) and the left rudimentary horn pregnancy (R. H. P).
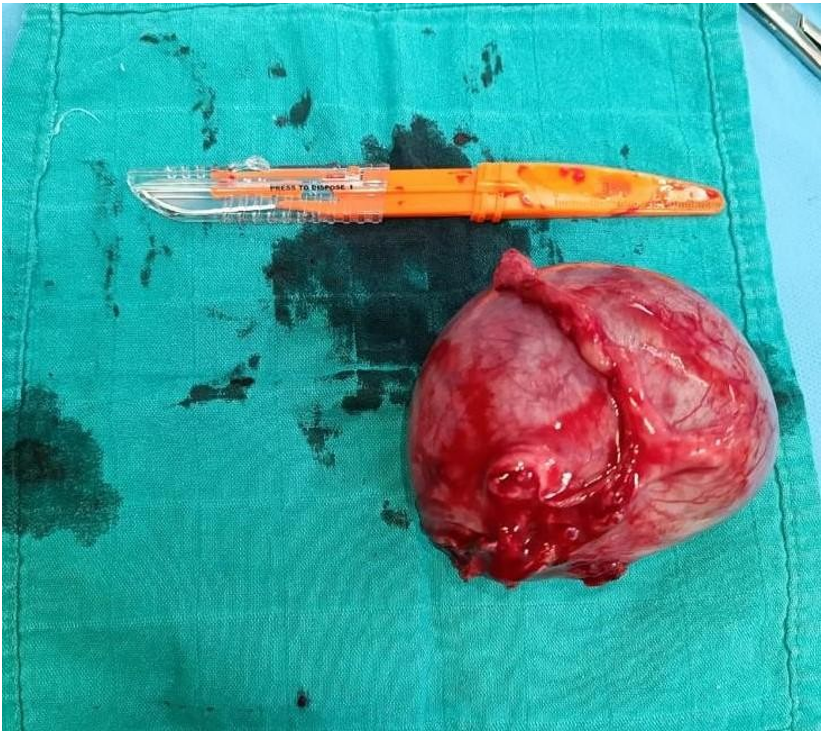
Figure 5: Shows the excised rudimentary horn pregnancy with fallopian tube.
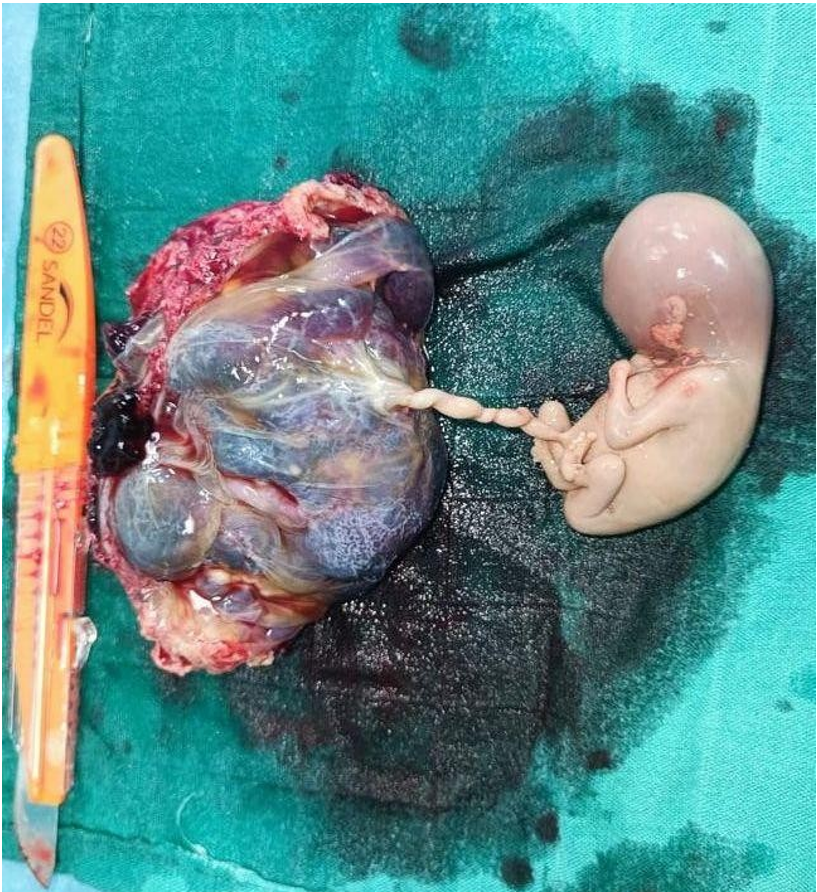
Figure 5: Shows the excise of rudimentary horn with fallopian tube and the fetus with the placenta.
Discussion
Unicornuate uterus is extremely rare. it presents 1/76,000 to 1/140,000 of pregnancies [2,7,10,11]. However, its occurrence is serious and may involve the vital maternal pc; its natural evolution is the almost inevitable rupture of the rudimentary hemiuterus in 80-90% occurring
frequently in the 2nd trimester [2,3,5,7,12,14]. This implies its early diagnosis at the very beginning of pregnancy allowing its early termination at the pre-rupture stage. However, the diagnosis of this type of ectopic pregnancy is laid in more than 50% at the rupture stage [12-14] nahum et al analyzed 588 cases of pregnancies on rudimentary horn having been reported in the literature between 1900 and 1999, the diagnosis was made at the rupture stage in 50%; having occurred in 80% before the 3rd trimester [10]. Seema et al reported 10 cases of uterine rupture in a retrospective analysis of 12 pregnancies on rudimentary horn [19]. 3 cases of uterine rupture in the 2nd trimester (20wk, 17wk, 24wk) were reported by Sujata et al in their retrospective analysis of 5 cases of rudimentary horn pregnancy admitted to their hospital between 2001 and 2010 [22].
This diagnostic delay can be justified by the fact that this rare ectopic pregnancy occurs in women whose uterine congenital malformation is not yet known and who have a history of normal pregnancies [2,12,13,16]. On ultrasound the pregnancy in a rudimentary horn can simulate a pregnancy of normal intrauterine
location due to the non-visualization of the normal hemiuterus latero-deviated by the gravid horn or take the appearance of a pregnancy in a bicornuate uterus.
pregnancy in a rudimentary horn can also be visualized on ultrasound as a latero-uterine pregnancy evoking a cornual, tubal or abdominal pregnancy, however, even if the diagnosis in this case is not established, it is indeed of an ectopic pregnancy systematically indicating a termination of pregnancy and therefore the therapeutic management is done at the pre-rupture stage. this is the case of our patient whose pregnancy was diagnosed as ectopic on ultrasound without suggesting a rudimentary horn pregnancy.
The sensitivity of ultrasound in the diagnosis of pregnancy on rudimentary horn of a unicornuate uterus is only 30% [8,12,16,17].
Tsafir proposes 3 sonographic criteria of strong suspicion of this type of ectopic pregnancy (19): a) pseudo asymmetric aspect of bicornuate pregnancy b) gestational sac surrounded by a layer of myometrium c) non-continuity of the gravid cavity with the cervical canal. The analysis of the ultrasound aspect of the pregnancy in our case shows the presence of a layer of musculature.
Magnetic resonance imaging, considered the gold standard in the diagnosis of uterine malformations, confirms the diagnosis [8,17,19]. Systematic termination of pregnancy is indicated in this type of ectopic pregnancy to prevent rupture of the rudimentary hemiuterus [8,9,12] even if sporadic cases of pregnancy carried to term are described in the literature [6,10]. management therapy consists of resection of the rudimentary horn with the homolateral fallopian tube.
Conclusion
Pregnancy on a rudimentary horn of a pseudo-unicorn uterus is certainly rare but must be well known; any delay in diagnosis can jeopardize the maternal prognosis. Thus, the obstetrician must be very attentive to the 1st obstetric ultrasound so as not to be trapped by this type of ectopic pregnancy.
References
- Li X, Peng P, Liu X, Chen W, Liu J, Yang J, et al. The pregnancy outcomes of patients with rudimentary uterine horn: A 30-year ex PMCID: PMC 6347 perience. PLoS One, 2019; 14(1): e0210788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210788. PMID: 30682068; PMCID: PMC6347.
- Ghotra MK Jr, Joshi B, Bhutani Ruptured Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy: Delayed Diagnosis. Cureus. 2021; 13(6): e15873. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15873. PMID: 34327098; PMC ID: PMC8302455.
- Ağaçayak E, Peker N, Yavuz M, Fındık FM, Evsen MS, Gül Rudimentary horn pregnancy - ten years of experience. Ginekol Pol, 2020; 91(3): 117-122. doi: 10.5603/GP.2020.0027. PMID: 32266951.
- Mengistu K, Bobe T, Tilahun G, Kifle K, Geleta D. Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy Diagnosed after Case Rep Obstet Gynecol, 2020; 2020: 5816487. doi: 10.1155/2020/5816487. PMID: 32774959; PMCID: PMC7396123.
- Houmaid H, Hilali Rupture of Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy at 16 Weeks of Gestation. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol, 2021; 2021: 8829053. doi: 10.1155/2021/8829053. PMID: 33505745; PMCID: PMC7815397.
- Zhang Y, Pang Y, Zhang X, Zhao Z, Liu Full-term pregnancy in a rudimentary horn with a live fetus: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore), 2020; 99(34): e21604. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021604. PMID: 32846770; PMCID: PMC7447397.
- Siwatch S, Mehra R, Pandher DK, Huria A. Rudimentary horn pregnancy: a 10-year experience and review of Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2013; 287(4): 687-95. doi: 10.1007/s00404-012-2625-7. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PMID: 23183713.
- Jomaa S, Ahmad A, Adwan D. Successful diagnosis and management of prerupture rudimentary horn pregnancy in the second trimester: a case Radiol Case Rep, 2021; 16(10): 3068-3071. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.07.044. PMID: 34429804; PMCID: PMC8365452.
- Kozar N, Serdinšek T, Tašner T, Reljič M, Gavrić Lovrec V, Kovač Diagnosis and management of rudimentary horn pregnancy rupture, misinterpreted as bicornuate uterus in the 14th week of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2021; 47(2): 843-846. doi: 10.1111/jog.14586. Epub 2020 Dec 3. PMID: 33271628.
- Nahum GG. Rudimentary uterine horn The 20th-century worldwide experience of 588 cases. J Reprod Med, 2002; 47(2): 151-163. PMID: 11883355.
- Mishra N, Yadav N, Koshiya D, Jhanwar Ruptured rudimentary horn pregnancy with a history of an uneventful vaginal delivery. J Med Ultrasound (2001), 2015; 42(1): 117-120. doi: 10.1007/s10396-014-0582-4. Epub 2014 Oct 17. PMID: 26578500.
- Rajbhandary S, Das A, Rai M, Sah AK. Rupture of Non-communicating Rudimentary Horn Pregnancy at 15 Weeks with Previous Normal Pregnancies: A Case JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc, 2020; 58(228): 614-617. doi: 10.31729/jnma.5104. PMID: 32968300; PMCID: PMC7580373.
- Demishev M, Avila C, Figueroa R, Hellinger JC, Ogburn Successful pregnancy outcome after conservative management of second-trimester cornual uterine rupture. J Ultrasound Med, 2014; 33(11): 2037-2039. doi: 10.7863/ultra.33.11.2037. PMID: 25336493.
- Sarikaya S, Aybay Uterine rupture of a patient with rudimentary horn pregnancy at 26th gestational weeks. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2022; 94: 107003. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107003. Epub 2022 Mar 29. PMID: 35405513; PMCID: PMC9006326.
- Bruand M, Thubert T, Winer N, Gueudry P, Dochez Rupture of Non-communicating Rudimentary Horn of Uterus at 12 Weeks' Gestation. Cureus, 2020; 12(3): e7191. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7191. PMID: 32269871; PMCID: PMC7135721.
- Souza CS, Dorneles GG, Mendonca GN, Santos CMD, Gallarreta FMP, Konopka CK. Pregnancy in Non-Communicating Unicornuate Uterus: Diagnosis Difficulty and Outcomes - a Case Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet, 2017; 39(11): 640-644. English. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607046. Epub 2017 Oct 3. PMID: 28973711.
- Mavrelos D, Sawyer E, Helmy S, Holland TK, Ben-Nagi J, Jurkovic D. Ultrasound diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy in the non-communicating horn of a unicornuate uterus (cornual pregnancy). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 2007; 30(5): 765-770. doi: 10.1002/uog.5131. PMID:
- Souza CS, Dorneles GG, Mendonça GN, Santos CMD, Gallarreta FMP, Konopka CK. Pregnancy in Non-Communicating Unicornuate Uterus: Diagnosis Difficulty and Outcomes - a Case Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet, 2017; 39(11): 640-644. English. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1607046. Epub 2017 Oct 3. PMID: 28973711.
- Chopra S, Keepanasseril A, Rohilla M, Bagga R, Kalra J, Jain Obstetric morbidity and the diagnostic dilemma in pregnancy in rudimentary horn: retrospective analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2009; 280(6): 907-910. doi: 10.1007/s00404-009-1013-4. Epub 2009 Mar 13. PMID: 19283398.
- Tsafrir A, Rojansky N, Sela HY, Gomori JM, Nadjari M. Rudimentary horn pregnancy: first-trimester prerupture sonographic diagnosis and confirmation by magnetic resonance imaging. J Ultrasound Med. 2005; 24(2): 219-223. doi: 10.7863/jum.2005.24.2.219. PMID:
- Dhanawat J, Pape J, Stuhlmann-Laeisz C, Maass N, Freytag D, Gitas G, et al. Ectopic pregnancy in noncommunicating horn of unicornuate uterus: 3D-ultrasound and primary laparoscopic management. Clin Case Rep, 2021; 9(5): e04261. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4261. PMID: 34084520; PMCID:
- Siwatch S, Mehra R, Pandher DK, Huria A. Rudimentary horn pregnancy: a 10-year experience and review of Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013: 287(4): 687-695. doi: 10.1007/s00404-012-2625-7. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PMID: 23183713.

