Impact of Air Pollution on Human Health
Shweta Bhodiwal*, Monu Yadav, Tansukh Barupal
Department of Botany, IIS University & KNHPI, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Department of Botany, MLSU, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India
S.B.K. Govt. P.G College Jaisalmer Rajasthan, India
Received Date: 21/03/2022; Published Date: 01/04/2022
*Corresponding author: Shweta Bhodiwal, Department of Botany, IIS University & KNHPI, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Abstract
Air pollution is a main concern issue of new civilized world, which toxicologically affects human wellbeing and the environment. It has various different discharge sources, yet engine vehicles and industrial processes contribute the significant part of air pollution. Air pollutants, like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), ozone (O3), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), heavy metals, and particulate matter, vary in their chemical composition, reaction properties, time of disintegration, emission, and capacity to diffuse in short or long distances. Long- and short-term exposure to air suspended poisons toxicologically affects human including respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses, neuropsychiatric complexities, the eyes irritation, skin diseases, and long-term chronic diseases as like cancer. Air contamination has both intense and chronic effects for human wellbeing, affecting the different systems and organs. Air pollution is thus considered as a major environmental risk factor in the incidence as well as progression of some diseases like asthma, ventricular hypertrophy, lung cancer, and Parkinson’s diseases, autism, psychological complications, retinopathy, fetal growth, and low birth weight, etc. What's more, short-and long-term exposure have additionally been connected with premature mortality and reduced life expectancy. These impacts of air pollutants on human wellbeing and their mechanism of the actions are briefly discussed.
Introduction
Various physical activities as like volcanoes, fire, and so forth may deliver various pollutants in the environment; anthropogenic exercises are the significant reason for natural air pollution. Dangerous chemicals can escape the environment by accident, however various air pollutants are let out of modern industries and different activities and may cause unfavorable impacts on human wellbeing (Kampa and Castanas 2008) [1] and thus it contributes to the range of health problems as like respiratory and cardiovascular diseases (Heal et al., 2012) [2].
A new report has revealed the relationship between male infertility and air pollution (Zhou et al., 2014) [3]. Cities give open doors to access centralized services, yet this frequently accompanies a variety of outcomes including noise, air, and light pollution. Focusing on the ambient air quality, exceedances of direction levels set by the World Health Organization (WHO) are clear and connected with an expected 6.5 million unexpected premature deaths worldwide every year, most of which are suffered by metropolitan populations (Landrigan et al., 2018) [4]. Around 4.3 million people die from the household air contamination and 3.7 million from surrounding air pollution, the greater part of whom (3.3 and 2.6 million, respectively) lives in Asia (Air pollution: Consequences and actions for the UK, and beyond. Lancet 2016; 387: 817.). In Iran, as a non-industrial nation, the degree of air pollutants has expanded progressively since the start of industrialization during the 1970s, yet it has arrived at an extremely unsafe level in some megacities like Mashhad, Tehran, Tabriz, Ahvaz, Arak, Isfahan, and Karaj throughout recent many years. Iran is the world's third fundamental dirtied country on the planet, which brings about 16 billion $ yearly loss (http://www.who.int/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/ databases/cities-2011/en/).
In this way, it is of great importance to describe the issue, especially its poisonous consequences for human wellbeing and give suggestions as a basis for ecological rules and standard conventions in the field of air pollution.
PSI & AQI
The Pollutant Standard Index (PSI) is a mathematical worth and signs of pollutant that is regularly used to facilitate risk assessment. It is a numeric value between zeros to 500 (According to U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). PSI is a rule for reporting the air quality which was first presented by Thom and Ott in 1974 (Thom & Ott, 1975) [5]. Hence, it would give a strategy for comparing the relative contribution of each of the pollutant to the total risk (Cairncross et al., 2007) [6]. The computation of PSI depends on the grouping of five significant air pollutants including particulate matters (PMs), carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) in the air.
As indicated by Johnson et al., " Air Quality Index (AQI) is characterized as a proportion of the state of air relative to the requirements of at least one biotic animal category or to any human need "(Johnson et al., 1997) [7]. AQI is divided into the ranges, in which they are numbered, and each range is marked with the color codes. It gives a number from healthy standard level of zero to a hazardous degree of over 300 to demonstrate the degree of wellbeing risk related with air quality.
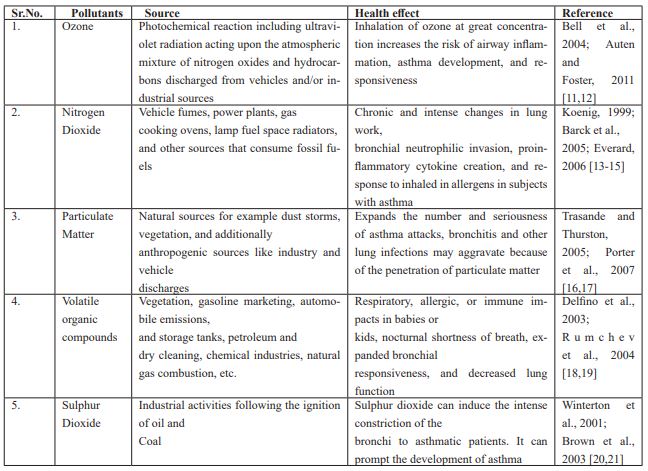
Table 1: Chemical pollutants and their heath impact.
Toxicity of Air Pollution
Impacts of air pollutants on living life will not only be restricted to the human and animal health yet also includes the whole environment. Different geological circumstances, worldwide environment changes, and the ecological varieties influence the human wellbeing and the environment including the animal life.
It is accounted for that exposure to outdoor airborne pollutants like nitrogen dioxide (NO2), Ozone(O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulates have the adverse effects on immune competent cells and the airway responsiveness (Delfino et al., 2009; Duki et al., 2003; Jerrett et al., 2005) [8-10]. These outdoor airborne pollutants are thus known to be released from both portable (road and off-road vehicles, aircraft and ships) and stationary sources (power plants, producing businesses, squander stores, agribusiness, volcanoes, woods fires, and so forth). Some of these chemicals can also be produced indoors, in spite their concentrations can fluctuate depending on the kind of source activities. In addition, aeroallergens are additionally conveyed and conveyed by parasitic spores or by particles of various origins. In Table 1, the source of outside allergens and their health impacts are summed up.
Ozone
As the main part of metropolitan brown haze, O3 is formed by the photochemical reaction in the ambient air through interaction with the nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons transmitted from traffic or potentially industrial sources (U.S. Natural Protection Agency, U.S. EPA, 2006) [22]. Due to the possibility to to sensitize the airway inflammation or damage lung tissues, ozone can cause many types of the breathing issues including wheezing, coughing and chest pain (Szyszkowicz et al., 2012; Trasande and Thurston, 2005; Xu et al., 2011) [16,23,24]. It can likewise build the resistant reaction to allergens in certain people (Auten and Foster, 2011). Roughly 40-60% of the inhaled O3 is absorbed in the nasal airways, while the rest of can reach at the lower airways (Bosson et al., 2008) [25], Bayram et al. (2001) [26] demonstrated that O3 and NO2 modulate airway inflammation, while stimulating the release of the inflammatory mediators from bronchial epithelial cells. In addition, O3 can likewise provoke a dose-dependent expansion in intracellular reaction oxygen species and in epithelial cell permeability. Inhaled allergens and poisons may then activate the release of the inflammatory cells along with their products (tumour necrosis factor, interleukin (IL)-1, -6, -8 etc.) (Auten and Foster, 2011; Bell et al.,2004) [11,12]. The impact of ozone exposure has been explored under the high (0.4 ppm) (Kreit et al., 1989) and low (0.16 ppm) levels for a prolonged duration (7.6 h) (Horstman et al., 1995) [27]. The outcomes reliably showed sensitive reactions in asthmatic subject’s comparative with healthy controls.
Nitrogen Oxides
Nitrogen oxides are significant ambient air poisons which might build the risk of respiratory infections (Chen et al., 2007) [28]. They are fundamentally transmitted from engine motors and subsequently are traffic related air pollutants. They are profound lung irritants that can prompt pulmonary edema if it has been inhaled at the high levels. They are normally less poisonous than O3, but NO2 can pose clear toxicological issues. Hacking and wheezing are the most widely recognized difficulty of nitrogen oxides poisonousness; however, the eyes, nose and throat irritations, migraine, dyspnea, chest pain, fever, diaphoresis, bronchospasm, and pulmonary edema may likewise happen. In another report, it is recommended that the degree of nitrogen oxide somewhere in the range of 0.2 and 0.6 ppm is harmless for the human population (Hesterberg et al., 2009) [29].
Particulate Matter
Particulate Matter (PM) is a heterogeneous combination of particles comprising of soil, sediment, smoke, and, surprisingly, liquid droplets too (aerosols) released from diverse natural as well as anthropogenic sources, for e.g., factory smokestacks, diesel-fueled motors, as well as power generation, mining, construction, and agricultural activities (Chen et al., 2008; Rosenlund et al., 2011; Son et al., 2011) [30-32]. As the particles can easily penetrate into lungs and then they increase the frequency and seriousness of asthma attacks. The penetration of PM can consequently irritate bronchitis and other lung infections while lessening the body's capacity to fight diseases (Trasande and Thurston, 2005) [16]. In animal experiments, the pollution status of the PM-bound progress metals (e.g., chromium, zinc, copper, cobalt, manganese, titanium, nickel, vanadium, and so on) was strongly connected with the degree of extent of radical activation and lung injury (Kleinman et al., 2007) [33].
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCS)
Numerous VOCs comprise the vital parts of various materials utilized in the livelihood facilities, for example, interior furnishings, pesticides, office equipment, cleaners, textiles and personal care supplies (Uhde and Salthamme, 2007) [34]. For instance, intense effects are known to happen by exposure to VOCs because of the utilization of diverse spray products that contain different kinds of VOCs. Specifically, Zock et al. (2007) [35] observed that the frequent utilization of the household cleaning sprays known to radiate different VOCs types can prompt a 40% increment in wheeze and a 50% increase in the asthma symptoms. Thusly, openness to VOCs has been designated as the essential speculate causing a number of asthma and asthmatic symptoms including breathlessness, suppressed lung function, and increased bronchial responsiveness (Rumchev et al., 2004) [19]. In different investigations, VOCs were likewise seen to induce the airway obstruction and inflammation (Delfino et al., 2003; Rumchev et al., 2004) [18,19].
Sulfur Dioxide
SO2 is a colorless and profoundly reactive gas, which is considered as a significant air pollutant. It is generally radiated from fossil fuel consumption, industrial cycles and natural volcanic activities. SO2 is extremely hurtful for vegetation, creature, and human health. Individuals with lung illness, kids, older people, and the people who are more exposed to the SO2 are at greater risk of the skin and lung diseases. The significant health concerns related with exposure to high concentration of the SO2 incorporate dysfunction and respiratory irritation, and furthermore irritation of existing cardiovascular illness. SO2 is dominatingly absorbed in upper airways. The penetration of SO2 into the lungs is more during mouth breathing as compared to the nose breathing. An expansion in the airflow in deep, quick breathing enhances the penetration of gas into the more profound deeper lung. Subsequently, individuals who exercise in the contaminated air would inhale more SO2 and are probably going to experience the greater irritation. Exposure to SO2 can make harm the eyes (corneal opacity and lacrimation), mucous layers, the skin (redness, and rankles), and respiratory tracts. Bronchospasm, pneumonitis, pulmonary edema and acute airway obstruction are the most widely recognized clinical discoveries related with exposure to SO2 (Chen et al., 2007; Ghorani-Azam et al., 2016) [28,36].
Measures to Control the Air Pollution
- Activated carbon is one of the most well-known form of air pollution control. This kind of control includes the utilization of a pollution filter, carbon, to lessen the number of pollutants that are permitted to escape into the air. When being used, these channels ingest pollutant that helps to clean the quality of any possible toxins.
- Biofiltration is one more viable kind of air pollution control. It utilizes microorganisms, regularly bacteria and fungi, to disintegrate toxins. Enterprises that utilize biofiltration systems include food and waste plants, drug organizations, and wastewater management facilities. While this technique for air pollution controls functions admirably, a large space is expected to operate a bio filtration framework. Numerous industries don't have this measure of accessible space, so this strategy is often disregarded.
- Change in Fuel: This method includes the utilization of less contaminating fuel to decrease air pollution. Utilization of low sulfur fuel rather than high sulfur fuel by electric utilities is an illustration of this strategy. Remember that low sulfur fuel is considerably more costly than high sulfur fuel. The other decision for an electric utility can be the utilization of natural gas as a fuel. Fuel switching based meteorological circumstances or air pollution estimates have been utilized to prevent air pollution issue in numerous areas.
- Utilization of oil with low ash content or natural gas for a dryer at a asphalt plant to lessen particulate matter is one more illustration of this strategy. Presentation of compressed natural gas, propane, ethanol and oxygenated fuels for vehicles have helped in the decrease of air pollutants
- Nuclear power plants are somewhat contamination free as compared with the coal fired power plants. However, they have been subjects of the controversy in their overall ecological effect (Kumar, S., & Katoria 2013; Ghorani-Azam et al, 2016) [36-42].
Conclusion
Air contaminations significantly affect human wellbeing, triggering, and prompting numerous diseases leading to the high morbidities and mortalities, especially in the developing nations.
Hence, air pollution control is vital and should be on the highest priority of the governments. The policy makers and officials in the nation should refresh all regulations and guidelines connected with air pollution. Coordination between various offices including in air pollution should be leaded by a strong environmental security association. A powerful environmental security association ought to have enough budget plans for organization, research, improvement, checking, and full control of the environment including air pollution.
Conflict of Interest: No
References
- Kampa M, Castanas E. Environmental Pollution, 2008; 151: 362e367.
- Heal MR, Kumar P, Harrison RM. Particles, air quality, policy and health. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012; 41(19): 6606-6630.
- Zhou N, Cui Z, Yang S, Han X, Chen G, Zhou Z, et al. Air pollution and decreased semen quality: a comparative study of Chongqing urban and rural areas. Environmental Pollution, 2014; 187: 145-152.
- Landrigan PJ, Fuller R, Acosta NJ, Adeyi O, Arnold R, Baldé AB, et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. The lancet, 2018; 391(10119): 462-512.
- Thom GC, Ott W. Air pollution indices: a compendium and assessment of indices used in the United States and Canada. The Council, 1975.
- Cairncross EK, John J, Zunckel M. A novel air pollution index based on the relative risk of daily mortality associated with short-term exposure to common air pollutants. Atmospheric environment, 2007; 41(38): 8442-8454.
- Johnson DL, Ambrose SH, Bassett TJ, Bowen ML, Crummey DE, Isaacson JS, et al. Meanings of environmental terms. Journal of environmental quality, 1997; 26(3): 581-589.
- Delfino RJ, Chang J, Wu J, Ren C, Tjoa T, Nickerson B, et al. Repeated hospital encounters for asthma in children and exposure to traffic-related air pollution near the home. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, 2009; 102(2): 138-144.
- Duki MZ, Sudarmadi S, Suzuki S, Kawada T, Tri-Tugaswatl A. Effect of air pollution on respiratory health in Indonesia and its economic cost. Archives of Environmental Health: An International Journal, 2003; 58(3): 135-143.
- Jerrett M, Arain A, Kanaroglou P, Beckerman B, Potoglou D, Sahsuvaroglu T, et al. A review and evaluation of intraurban air pollution exposure models. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 2005; 15(2): 185-204.
- Bell ML, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987-2000. Jama, 2004; 292(19): 2372-2378.
- Auten RL, Foster WM. Biochemical effects of ozone on asthma during postnatal development. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2011; 1810(11): 1114-1119.
- Koenig JQ. Air pollution and asthma. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology, 1999; 104(4): 717-722.
- Barck C, Lundahl J, Hallden G, Bylin G. Brief exposures to NO2 augment the allergic inflammation in asthmatics. Environmental Research, 2005; 97(1): 58-66.
- Everard ML. The relationship between respiratory syncytial virus infections and the development of wheezing and asthma in children. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006; 6: 56–61.
- Trasande L, Thurston GD. The role of air pollution in asthma and other pediatric morbidities. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology, 2005; 115(4), 689-699.
- Porter M, Karp M, Killedar S, Bauer SM, Guo J, Williams DA, et al. Diesel-enriched particulate matter functionally activates human dendritic cells. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology, 2007; 37(6): 706-719.
- Delfino RJ, Gong H, Linn WS, Hu Y, Pellizzari ED. Respiratory symptoms and peak expiratory flow in children with asthma in relation to volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath and ambient air. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 2003; 13(5): 348-363.
- Rumchev K, Spickett J, Bulsara M, Phillips M, Stick S. Association of domestic exposure to volatile organic compounds with asthma in young children. Thorax, 2004; 59(9): 746-751.
- Winterton DL, Kaufman J, Keener CV, Quigley S, Farin FM, Williams PV, et al. Genetic polymorphisms as biomarkers of sensitivity to inhaled sulfur dioxide in subjects with asthma. Annals of allergy, asthma & immunology, 2001; 86(2): 232-238.
- Brown TP, Rushton L, Mugglestone MA, Meechan DF. Health effects of a sulphur dioxide air pollution episode. Journal of Public Health, 2003; 25(4): 369-371.
- EPA U. Air quality criteria for ozone and related photochemical oxidants. Office, NC f. EA-R., Ed. US EPA: Research Triangle Park, 2006; 2.
- Szyszkowicz M, Porada E, Searles G, Rowe BH. Ambient ozone and emergency department visits for skin conditions. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 2012; 5(3): 303-309.
- Xu F, Yan S, Wu M, Li F, Xu X, Song W, et al. Ambient ozone pollution as a risk factor for skin disorders. British journal of dermatology, 2011; 165(1): 224-225.
- Bosson J, Barath S, Pourazar J, Behndig AF, Sandström T, Blomberg A, Ädelroth E. Diesel exhaust exposure enhances the ozone-induced airway inflammation in healthy humans. European Respiratory Journal, 2008; 31(6): 1234-1240.
- Bayram H, Sapsford RJ, Abdelaziz MM, Khair OA. Effect of ozone and nitrogen dioxide on the release of proinflammatory mediators from bronchial epithelial cells of nonatopic nonasthmatic subjects and atopic asthmatic patients in vitro. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2001; 107(2): 287-294.
- Horstman DH, Ball BA, Brown J, Gerrity T, Folinsbee LJ. Comparison of pulmonary responses of asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects performing light exercise while exposed to a low level of ozone. Toxicology and industrial health, 1995; 11(4): 369-385.
- Chen TM, Kuschner WG, Gokhale J, Shofer S. Outdoor air pollution: nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide health effects. The American journal of the medical sciences, 2007; 333(4): 249-256.
- Hesterberg TW, Bunn WB, McClellan RO, Hamade AK, Long CM, Valberg PA. Critical review of the human data on short-term nitrogen dioxide (NO2) exposures: evidence for NO2 no-effect levels. Critical reviews in toxicology, 2009; 39(9): 743-781.
- Chen G, Song G, Jiang L, Zhang Y, Zhao N, Chen B, et al. Short-term effects of ambient gaseous pollutants and particulate matter on daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Journal of occupational health, 2008; 50(1): 41-47.
- Rosenlund JD, Stanek LW, Luben TJ, Johns DO, Buckley BJ, Brown JS. Particulate Matter and Mortality among Survivors of Myocardial Infarction: Population-Based Cohort Study, 2011.
- Son JY, Bell ML, Lee JT. Survival analysis of long-term exposure to different sizes of airborne particulate matter and risk of infant mortality using a birth cohort in Seoul, Korea. Environmental health perspectives, 2011; 119(5): 725-730.
- Kleinman MT, Sioutas C, Froines JR, Fanning E, Hamade A, Mendez L, et al. Inhalation of concentrated ambient particulate matter near a heavily trafficked road stimulates antigen-induced airway responses in mice. Inhalation Toxicology, 2007; 19(sup1), 117-126.
- Uhde E, Salthammer T. Impact of reaction products from building materials and furnishings on indoor air quality—a review of recent advances in indoor chemistry. Atmospheric Environment, 2007; 41(15): 3111-3128.
- Zock JP, Plana E, Jarvis D, Antó JM, Kromhout H, Kennedy SM, Kogevinas M. The use of household cleaning sprays and adult asthma: an international longitudinal study. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 2007; 176(8): 735-741.
- Ghorani-Azam A, Riahi-Zanjani B, Balali-Mood M. Effects of air pollution on human health and practical measures for prevention in Iran. Journal of research in medical sciences: the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 2016; 21.
- Kumar S, Katoria D. Air Pollution and its Control Measures. International Journal of Environmental Engineering and Management, 2013; 4(5): 445-450.
- Air pollution: Consequences and actions for the UK, and beyond. Lancet, 2016; 387: 817.
- Kreit JW, Gross KB, Moore TB, Lorenzen TJ, D'Arcy JAMES, Eschenbacher WL. Ozone-induced changes in pulmonary function and bronchial responsiveness in asthmatics. Journal of applied physiology, 1989; 66(1): 217-222.
- Matter-induced health effects: who is susceptible? Environ Health Perspect 1999; 119: 446–54.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Metropolitan area trends. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; 1996.
- WHO. Database: Outdoor Air Pollution in Cities; 2003; 2010.

